Figure 3.
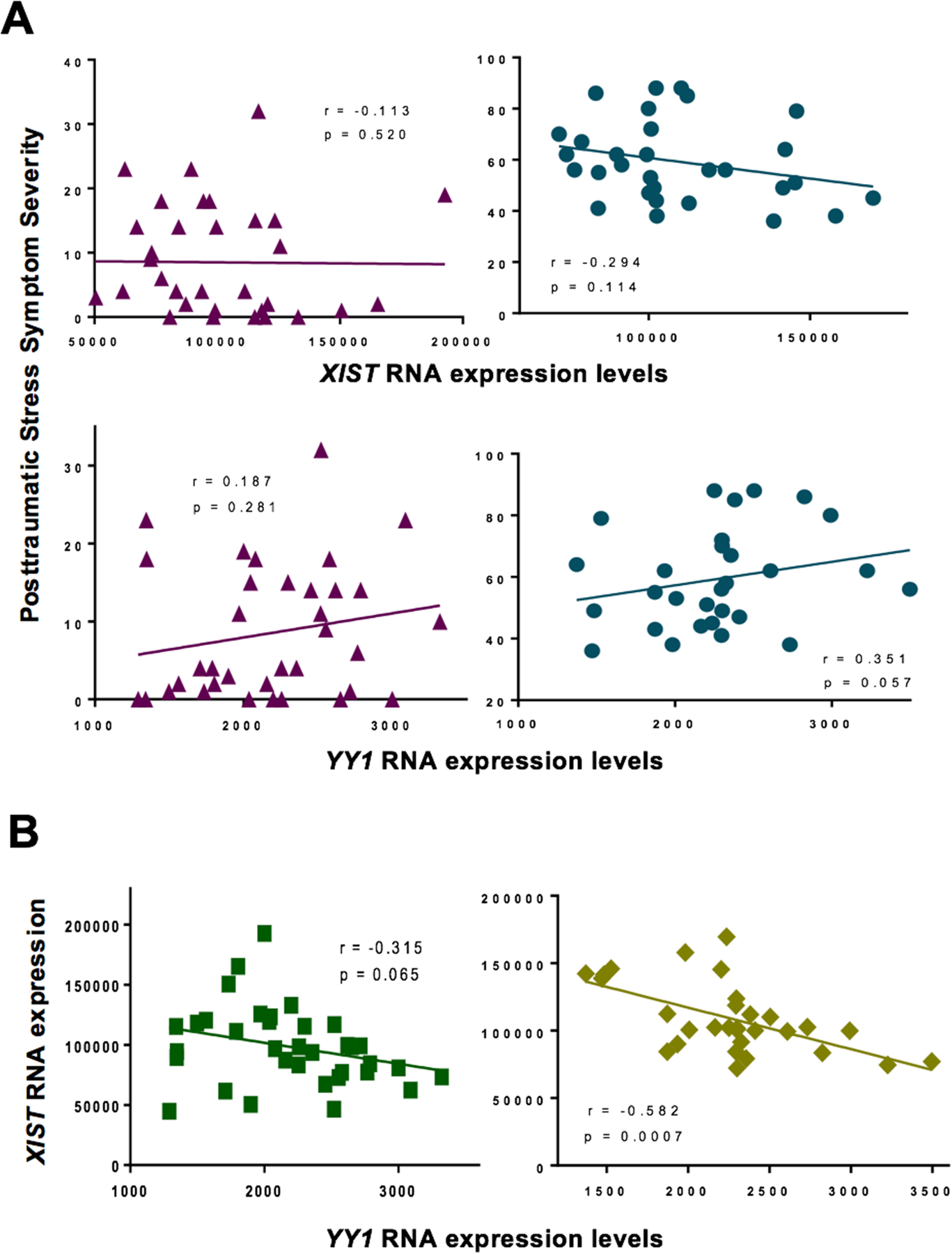
Relationship between RNA expression levels of key regulators of X Chromosome inactivation, XIST and YY1, and posttraumatic stress symptom (PTSS) severity scores in women following motor vehicle collision trauma. A) XIST RNA expression levels were examined in relation to PTSS severity scores in women who recovered following motor vehicle collision (top left, purple triangles, n=35), and in women who developed co-morbid CMSP and PTSS following motor vehicle collision (top right, teal circles, n=30). YY1 RNA expression levels were also analyzed in relation to PTSS severity scores in women who recovered following motor vehicle collision (bottom left, purple triangles, n=35), and in women who developed co-morbid CMSP and PTSS following motor vehicle collision (bottom right, teal circles, n=30). B) The relationship between XIST RNA expression levels and YY1 RNA expression levels in women who recovered following motor vehicle collision (left, green squares, n=35) and in women who developed co-morbid CMSP and PTSS following motor vehicle collision (right, yellow diamonds, n=30). RNA expression levels were measured via RNA sequencing of blood collected in the early aftermath of motor vehicle collision. Bivariate analyses were used to derive Spearman correlation coefficients and corresponding p values.
