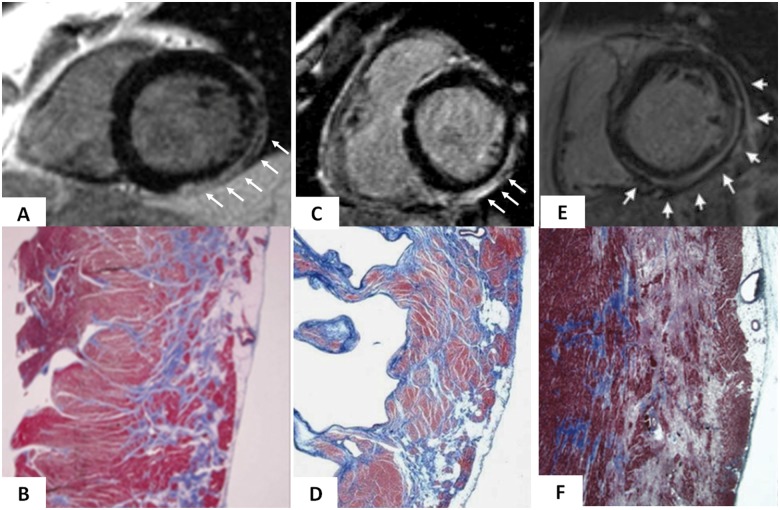
Figure 5.
Cardiac magnetic resonance features and histopathologic findings of non-ischaemic left ventricular scar of different aetiologies. Muscular dystrophy (A and B): post-contrast T1 inversion recovery sequence in short-axis view showing a subepicardial stria of late gadolinium enhancement in the left ventricular wall (white arrows) (A); corresponding panoramic histopathologic view of the inferolateral left ventricular wall showing replacement-type fibrosis confined to the outer-mid layer of the musculature (B). Modified from Yilmaz et al.71 Chronic myocarditis (C and D): post-contrast T1 inversion recovery sequence in short-axis view showing subepicardial late gadolinium enhancement of the inferolateral left ventricular wall (C); corresponding panoramic histopathologic view of the inferolateral left ventricular wall showing extensive fibrous tissue replacement in the subepicardial layer of the musculature (D). From Yilmaz et al.71 Desmosomal gene-related, left-sided arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (E and F): post-contrast T1 inversion recovery sequence in short-axis view showing subepicardial late gadolinium enhancement of the infero-lateral left ventricular wall in a DSP-gene mutation carrier (E). Panoramic histopathologic view showing myocardial replacement of the outer layer of the infero-lateral left ventricular wall in a sudden cardiac death victim carrying a DSP-gene mutation (F). From Zorzi et al.44