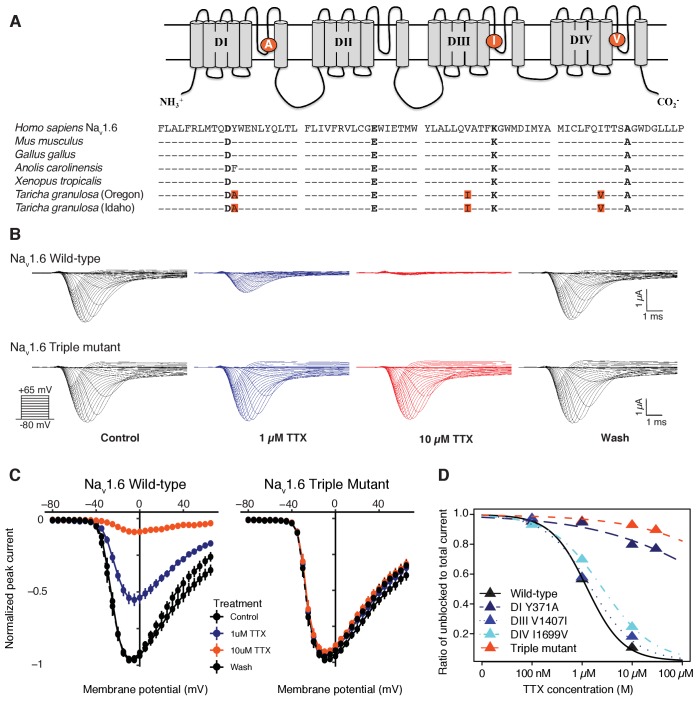
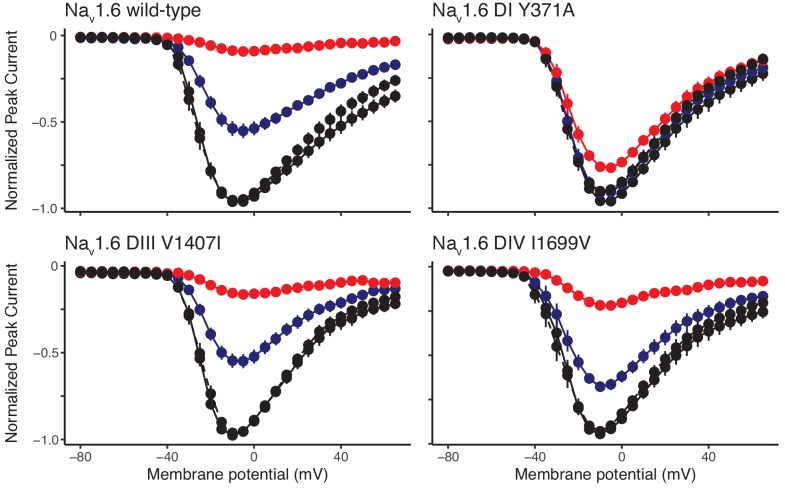
Figure 5. Newts possess Nav channel mutations that confer physiological resistance to TTX.
(A) Predicted topology of Nav1.6 with mutations in domains I, III, and IV. Sequence alignment of Nav1.6 pore-loop motifs revealed three amino acid differences in newts from Oregon or Idaho populations. (B) Representative currents from wild-type mouse Nav1.6 or Nav1.6 with newt substitutions Y371A, V1407I, and I1699V treated with 1 µM (blue) or 10 µM (orange) TTX. (C) Current-voltage (I–V) relationships showing normalized currents for wild-type (n = 21) and mutant Nav1.6 (n = 20) channels. Wild-type Nav1.6 was blocked by TTX (Tukey’s multiple comparisons test with Bonferroni correction: control vs. 1 µM, p<0.0001; control vs. 10 µM, p<0.0001), while mutated Nav1.6 was unaffected (repeated measures ANOVA, p=0.879). (D) Dose-response curves showing the proportion of Na+ current elicited during a step depolarization from −100 to −20 mV for wild-type, individual mutants, and triple-mutant Nav1.6 channels exposed to increasing concentrations of TTX. Sample sizes are provided in Table 2. Data were fit with a Hill equation to estimate IC50 values.