Figure 6. Supplementation with Lactobacillus reuteri 6475 prevents bone loss in post-antibiotic treated C57BL/6 male mice.
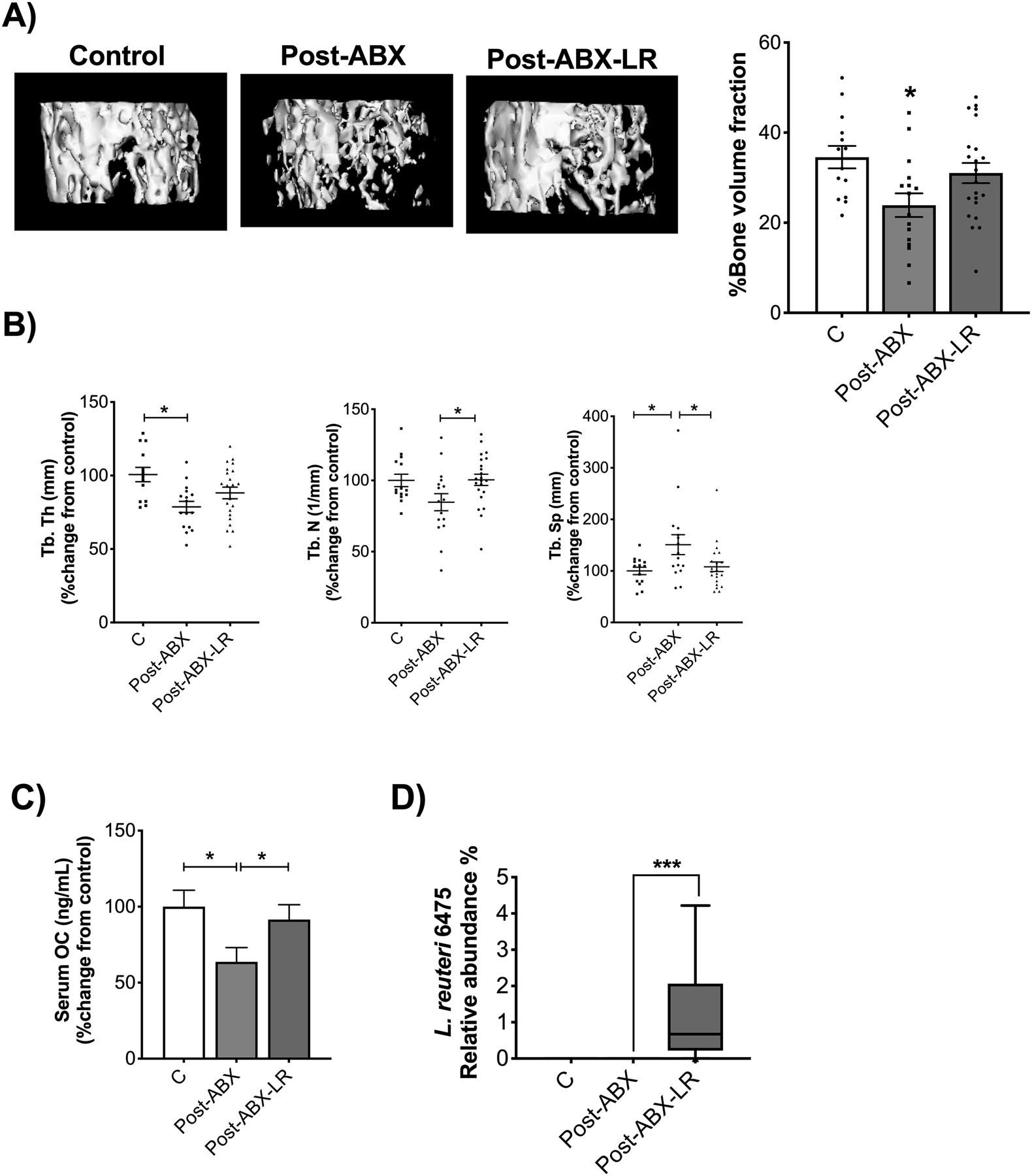
After treatment with ABX for two weeks WT male mice were untreated (natural repopulation, group shown in Fig 2) or treated with L. reuteri 6475 for four weeks. Note that the C and Post-ABX are the same as shown in Fig 2. These experiments were done together with the LR supplementation group. A) Representative micro-computed tomography isosurface images by uCT. B) Trabecular thickness (Tb. Th (mm)), trabecular number (Tb. N (1/mm)), and trabecular space (Tb. Sp (mm)) expressed as percentage change from control. C) Serum osteocalcin levels (OC (mg/mL)) expressed as percentage change from control. D) Analysis of relative abundance of L. reuteri 6475. Values represent mean ± standard error. n > 7 per group. Statistical analysis performed by T-test or 1-way ANOVA with Tukey post-test. *p<0.05 compared to control. Control and Post-ABX-LR are not significantly different. C: control, Post-ABX: antibiotic treated for 2 weeks followed by 4 weeks of no treatment, Post-ABX-LR: antibiotic treated for 2 weeks followed by 4 weeks of LR.
