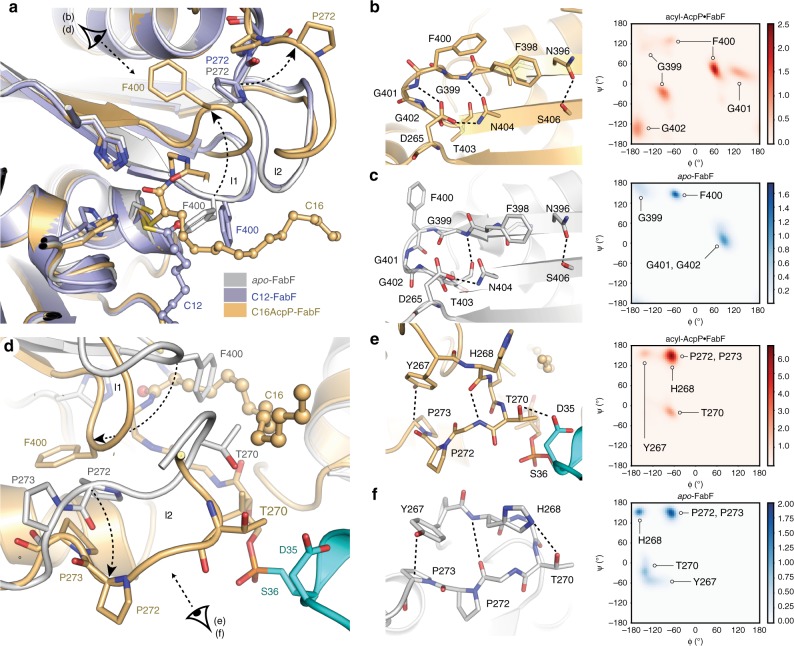
Fig. 5. Conformational changes in FabF active site loops.
a Comparison of F400, loop 1, and loop 2 conformations of apo-FabF (light grey, PDB: 2GFW43), dodecanoyl-FabF (light purple, PDB: 2GFY43), and C16AcpP–FabF (light orange, PDB: 6OKG). b Interactions that stabilize the open-conformation of the β-turn motif of loop 1 in C16AcpP–FabF and associated Ramachandran analysis of the conserved GFGG sequence within loop 1 from 1.5 μs of 10:0-AcpP·FabF, 12:0-AcpP·FabF, 16:0-AcpP·FabF (total of 4.5 μs) molecular dynamics (MD) simulation data. c Interactions that stabilize the closed-conformation of the β-turn motif of loop 1 in apo-FabF (light grey) and associated Ramachandran analysis of the conserved GFGG sequence within loop 1 from 1.5 μs of MD simulation data of apo-FabF. d Loop 2 overlay of apo-FabF (light grey, PDB: 2GFW) and C16AcpP–FabF (light orange) with the crosslinked AcpP colored cyan. e Interactions that stabilize the β-turn open conformation of loop 2 in C16AcpP–FabF (light orange) and associated Ramachandran analysis of key loop 2 residues of FabF monomers of acyl-AcpP·FabF complexes (gate-open conformation) from 1.5 μs of 10:0-AcpP·FabF, 12:0-AcpP·FabF, 16:0-AcpP·FabF (total of 4.5 μs) MD simulation data. f Interactions that stabilize the loop 2 closed conformation in apo-FabF (white) and associated Ramachandran analysis of key loop 2 residues of FabF of apo-FabF (gate-closed conformation) from 1.5 μs of MD simulation data of apo-FabF. a–f Residues are shown as sticks and colored according to element. Hydrogen-bond interactions are highlighted using dotted lines. b, c, e, f Simulated backbone φ and ψ dihedrals were binned using widths of 5°. Color bars indicates density of data points within each 2D bin.