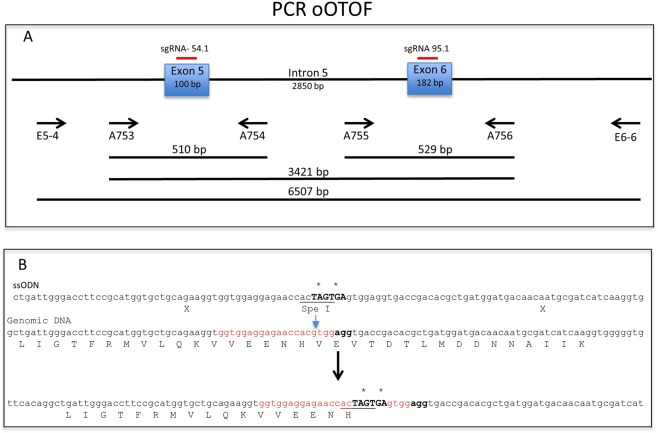
Figure 4.
oOTOF gene knock-out strategy. Panel a) Two sgRNA were designed to target exon 5 and exon 6 (sgRNA 54.1 and 95.1, respectively). Below, arrows mark the positions of the primers described in Supplementary Table 2 that were used for genotyping and lines the size of the different PCR products. Primers were designed to amplify each target zone to define if KO/KI happened in exon 5 or KO in exon 6. Large PCR were done to analyse if large deletion occured between exon 5 and 6. Panel b) A ssODN (108 bp) with short homology arms (51 bp each arm) was designed to introduce in exon 5 two premature stop codons (bold, back, marked with asterisks) and a restriction site (SpeI, underlined) to facilitate genotyping. Blue arrow is cleavage site of the genomic DNA by Cas9, 3 bp upstream of the PAM, AGG in lower case, bold). The restriction site insertion one base upstream of the cleavage site was designed to use the AC sequence to generate a SpeI site (ACTAGT) by the introduction of the two stop codons TAGTGA. In red, sequence recognized by sgRNA 54.1 on exon 5. The lower diagram shows the sequence after introduction of the two stop codons immediately upstream of the cleavage site. This sequences will alter transcription and will not be recognized by sgRNA 54.1.