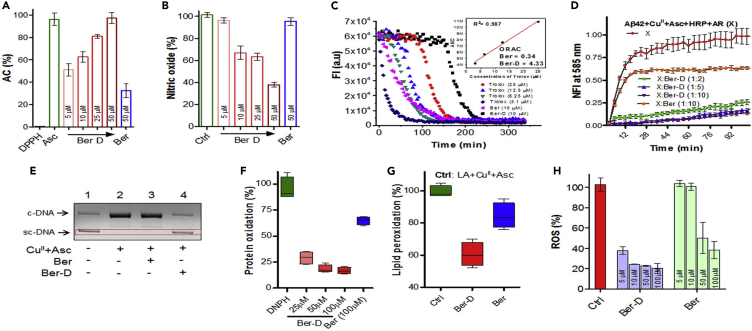
Figure 4.
In Vitro and In Cellulo Antioxidant Assay
(A and B) Radical scavenging property of Ber-D and berberine analyzed through DPPH (A) and nitric oxide (B) assay and plotted as their percentage of antioxidant capacity (% of AC) or nitric oxide percentage.
(C) Determination of oxygen radical quenching capacity (ORAC) value for Ber-D and berberine through ORAC assay with Trolox as internal standard.
(D) Resorufin fluorescence intensity (585 nm) measured in solutions of Aβ42 (5.1), CuII (5 μM), Asc (150 μM) HRP, and Amplex Red (10 μM) in presence of Ber-D or berberine with time for 100 min with incubation at 37°C.
(E) Agarose gel electrophoresis of plasmid DNA (pBR322, 2 μg/mL) treated with 20 μM of Ber-D or berberine and CuII (5 μM) in the presence of ascorbate (150 μM) incubated at 37°C. sc-DNA, supercoiled DNA; c-DNA, circular DNA.
(F) BSA (1 mg/mL), CuII (0.1 mM) and H2O2 (2.5 mM), Ber-D or berberine (0.1 mM) are added, and the percentage of BSA oxidation was assessed and quantified by measuring DNPH absorption at 370 nm.
(G) Linoleic acid (10 mM), CuII (0.1 mM), Ber-D or berberine (0.1 mM), and ascorbate (2 mM) are added, and the percentage of lipid peroxidation was assessed and quantified by measuring TBARS formation through absorbance change at 532 nm.
(H) Quantifying ROS generation in PC12 cells incubated with Aβ42 (10 μM), CuII (10 μM), Ber-D or berberine (10 μM), and ascorbate (200 μm) by measuring by DCF fluorescence intensity at 529. Each experiment was repeated three times (n = 3, n = 6 for DCFDA assay) and error bars represent the standard deviation (SD). Ber, berberine.
See also Figures S3 and S5.