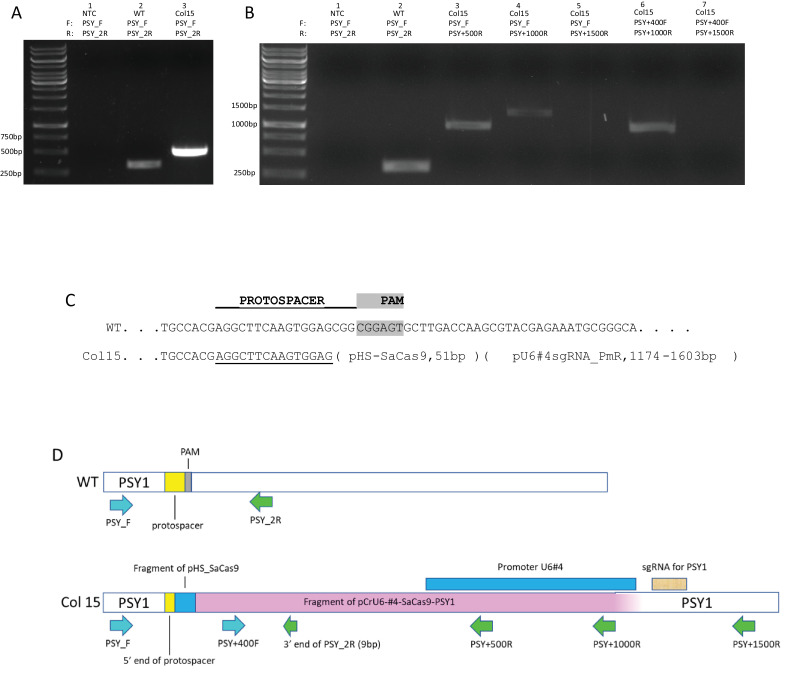
Fig. 2.
Insertion of plasmid sequence at PSY1 target site in one white colony transformant. (A) PCR products obtained for genomic DNA from recipient strain CC-3403 (WT) and from white Colony #15, using PSY1-specific primers PSY_F and PSY_2R. A product of the expected size (317 bp) was amplified for CC-3403 DNA, but a larger fragment was amplified for Colony #15. NTC, no template control. (B) After sequencing the white Colony #15 PCR product from (A), new reverse primers were used with PSY_F to determine the 3′ end of the insert. Products were obtained for primer sets containing PSY_F and PSY_R for CC-3403 (lane 2), PSY_F and either PSY+500R or PSY+1000R (lanes 3 and 4), and with PSY+400F and PSY+1000R (lane 6), but not for PSY_F or PSY+400F and PSY+1500R (lanes 5 and 7). (C) Schematic showing wild type sequence of PSY1 in region of targeted edit (middle), the protospacer and PAM (top), and the position of insertion of plasmid DNA fragments (as determined by PCR analysis shown in panel B and sequence analysis of PCR products) in PSY1 gene in white Colony #15. (D) Primer positions for PCR of CC-3403 (top) and Colony #15 (bottom) genomic DNAs. PCR results shown in panel B indicate that the right-most end of the insert fragment within PSY1 in Colony #15 must lie somewhere between the PSY+1000R and PSY+1500R primer binding sites (light purple to white rectangle in bottom schematic). PAM, protospacer-adjacent motif.