Figure 1.
Identification of the HOTAIR Conserved Noncoding Element (CNE) and Its Homolog in HOXD Cluster across Vertebrates
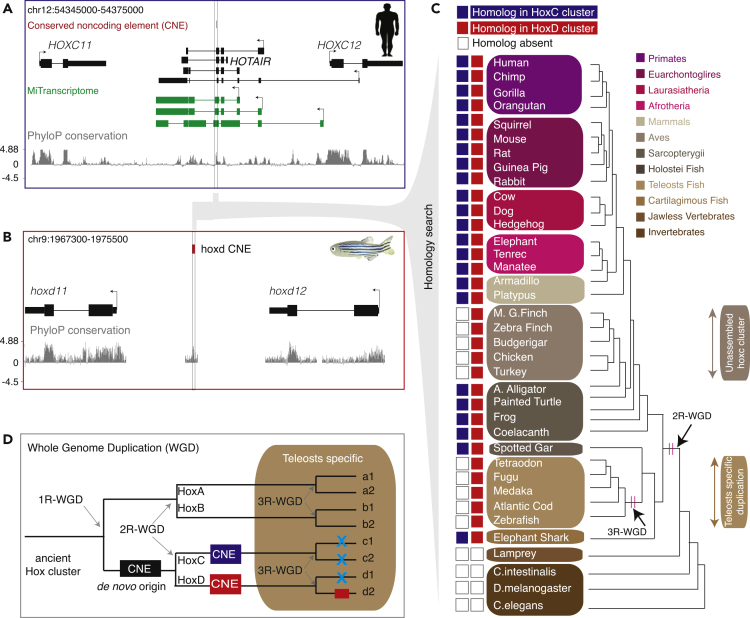
(A) A genome browser view around HOTAIR locus showing CNE from ANCORA browser and UCSC PhyloP conservation track. The CNE highlighted in a rectangular box is located eight nucleotides away from the splice site.
(B) The ortholog of the CNE mapped to the zebrafish hoxd (between hoxd11 and hoxd12) cluster.
(C) Homology search of the CNE across 37 species identified homologous CNEs in only HoxC and HoxD clusters. Homologs of the CNE are undetected in jawless vertebrate and invertebrates. Homologs in HoxC and HoxD clusters are represented by blue and red, respectively. Empty boxes indicate absence of homologs.
(D) Schematic representation for the proposed model of the origin of the CNE. The CNE might have a de novo origin in ancestral HoxC/D cluster where the second round of whole-genome duplication (2R-WGD) resulted two copies in HoxC and HoxD clusters. Teleost-specific duplication might have resulted in loss of CNE from both HoxC clusters and one of the HoxD cluster.