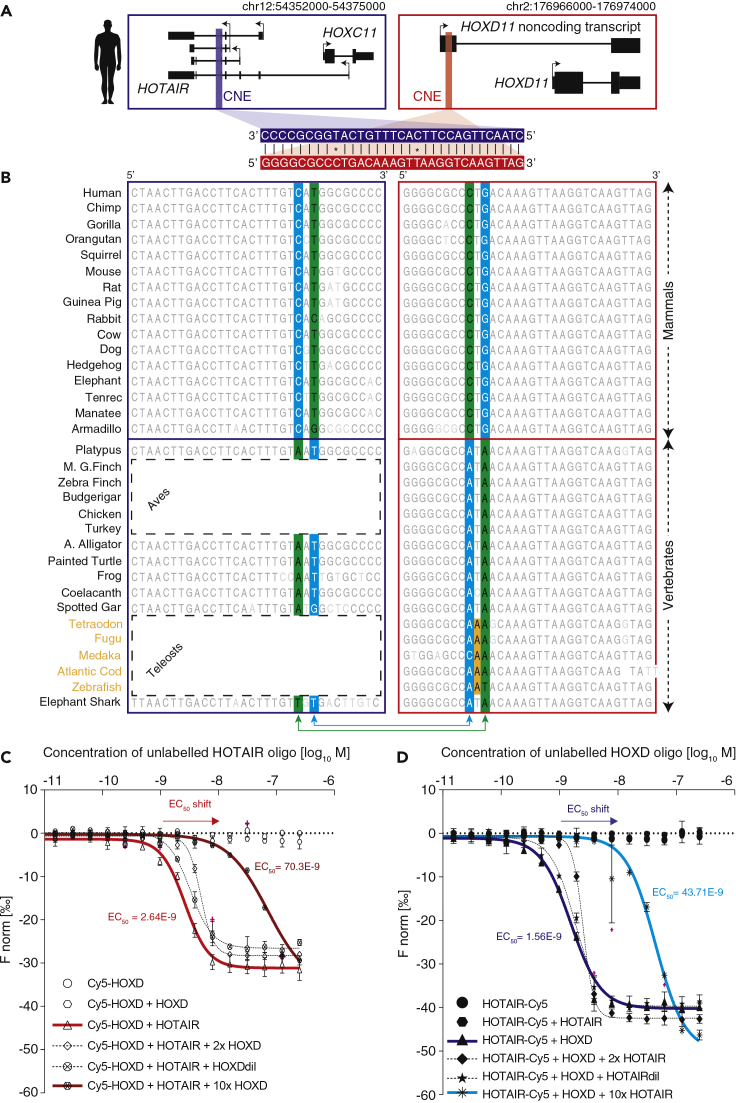
Figure 3.
Paralogous CNEs Exhibit Sequence Complementarity in Transcript Orientation
(A) Paralogous HOTAIR CNE (blue bar) and HOXD CNE (red bar) are zoomed and aligned in 5′ to 3′ orientation of respective transcripts.
(B) Alignment of the paralogous CNEs in 5′ to 3′ orientation of respective transcripts reveals sequence complementarity across vertebrates. Genetic substitutions within paralogous CNEs co-occurred at specific positions, which resulted in gain or loss of complementarity, where green represents non-complementary DNA and cyan represents complementary DNA. Teleost-specific change in DNA sequence is shown in orange.
(C and D) Microscale thermophoresis (MST) assay to evaluate the interaction between labeled and unlabeled RNA-oligos at different concentration. MST-on time of 5 s was used for analysis. Baseline-corrected normalized fluoresce (ΔFNorm) was chosen to present data (independent n ≥ 3 measurements; each point on the graphs presents mean ± SD). An extrapolated EC50 ± SD curve is fitted and shown on the graph. The concentration of the labeled RNA-oligo was constant at 5 nM. The concentration of unlabeled RNA-oligo was varied at 250 nM to 7.63 pM. The x axis represents the concentration of titrated unlabeled RNA-oligo. The y axis represents interaction-driven normalized fluorescence change (ΔFnorm[‰]). Measurement of interaction between (C) labeled HOXD CNE (Cy5-HOXD) RNA-oligo and unlabeled HOTAIR CNE RNA-oligo and (D) labeled HOTAIR CNE (HOTAIR-Cy5) RNA-oligo and unlabeled HOXD CNE RNA-oligo.