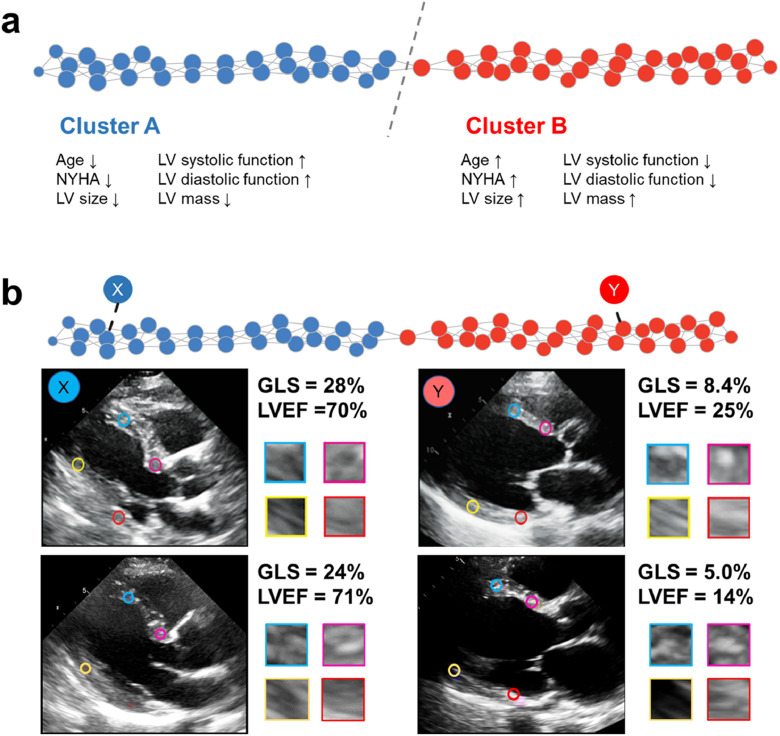
Fig. 2.
Patient similarity network based on myocardial texture features. Panel a: Extracted texture features were integrated using topological data analysis to create a patient similarity network. In the network, patients with similar features form a node, and adjacent nodes, including similar patients, are connected with edges. The network demonstrated the shape of a bar that was geometrically divided into two parts which had significantly different clinical and echocardiographic characteristics although the groups were created using only texture features. Panel b. Patients X, Y, Z, and W were identified in corresponding x, y, z, and w nodes, respectively. X and Y had a normal cardiac function and were found in cluster A, whereas Z and W were located in cluster B with significantly impaired cardiac function. GLS, global longitudinal strain; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction.