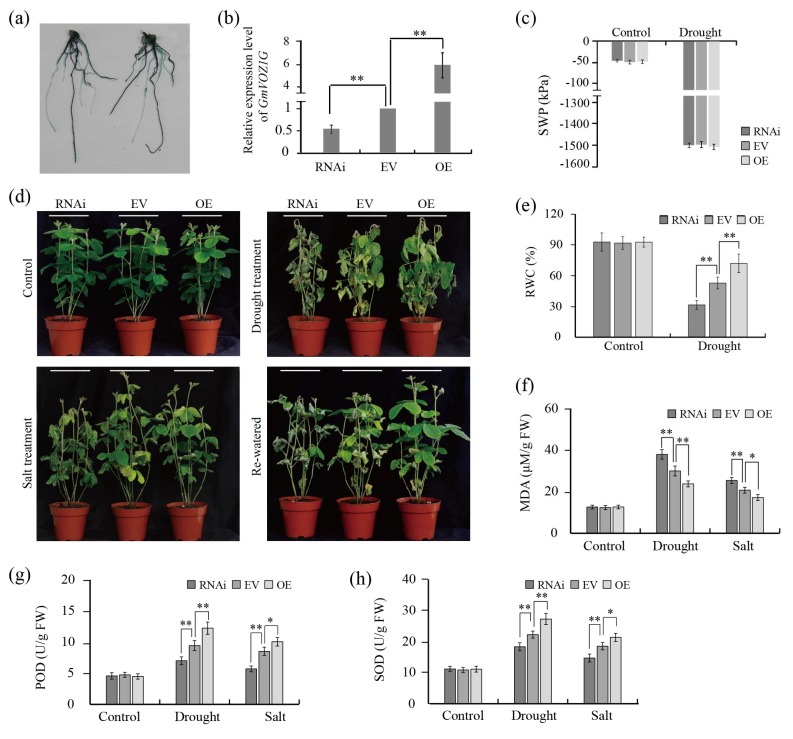
Figure 7.
Assessment of the effect of drought and salt stress on GmVOZ1G transgenic soybean hairy roots. (a). GUS detection of the transformation efficiency in soybean hairy roots. (b). qTR–PCR analysis of GmVOZ1G transcription levels in overexpression of GmVOZ1G, RNAi, and empty vector (EV) control soybean hairy roots. The expression level of tubulin was used as a quantitative control. The means of four biological replicates and the standard deviation are presented. (c). Soil water potential (SWP) was determined under normal and drought stress conditions. (d). Phenotypes of soybean composite seedlings with overexpression, RNAi, and EV control hairy roots under drought and salt stress treatments. (e−h). Relative water content (RWC), malondialdehyde (MDA) content, peroxidase (POD), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activities in leaves of soybean composite seedlings with different transgenic hairy roots under normal and stress conditions. All values are the means and SD of three independent replicates. The asterisks indicate statistical differences in comparison with the corresponding controls at p < 0.01 (**) and 0.01 < p< 0.05 (*), respectively.