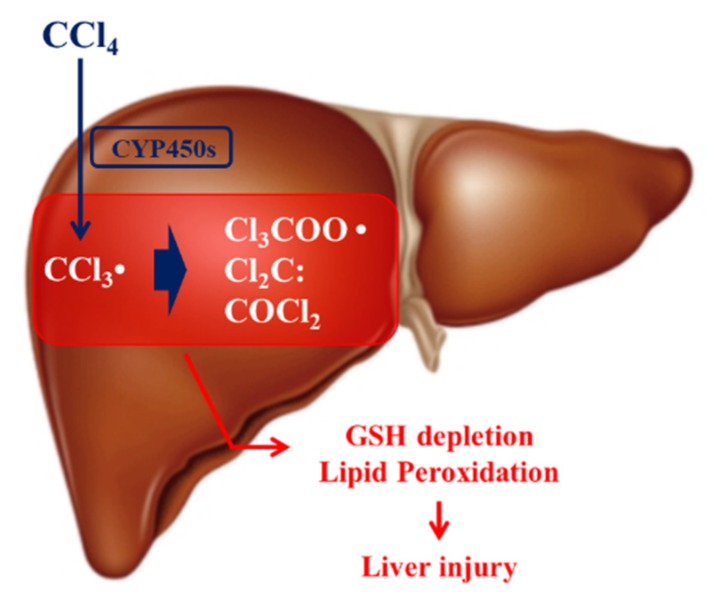
Figure 1.
Mechanism of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) hepatotoxicity. CCl4 is metabolized by cytochrome P450s (CYP450s) to CCl3•, which is further converted into Cl3COO•, Cl2C, and COCl2. These toxic metabolites are detoxified by glutathione (GSH). However, excessive exposure to CCl4 causes GSH depletion and oxidative stress via reactions, such as membrane lipid peroxidation that can cause liver damage.