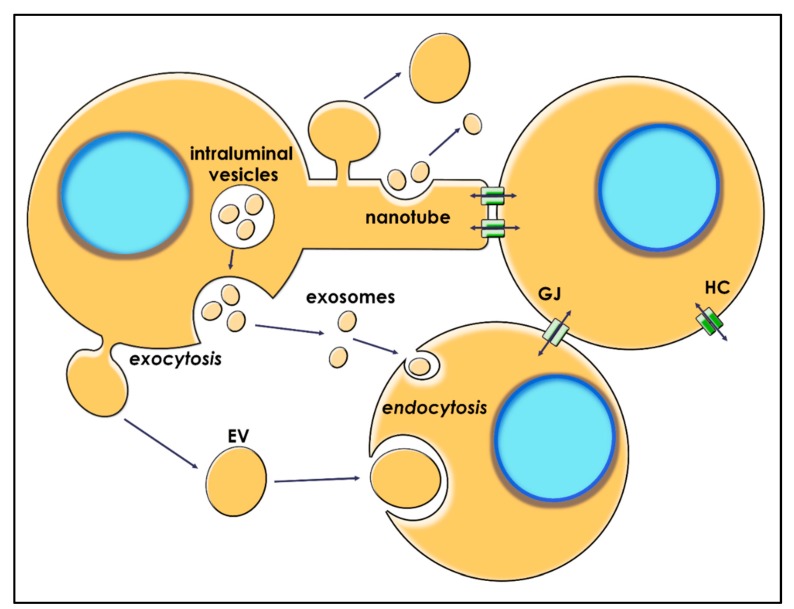
Figure 2.
The mechanisms of intercellular communication via miRNA. miRNA can be released as Ago2-bound miRNA or packaged in membrane structures (exosomes and extracellular vesicles). Exosomes and extracellular vesicles (EVs) are englobed by recipient cells through endocytosis or pinocytosis, and miRNAs exert their effects at this level. Cell-cell contact can be mediated by gap junctions (GJs) which directly transfer miRNA between adjacent cells. A similar mechanism is realized by nanotubes which permit direct contact at a distance. Connexins from GJs may also form hemichannels (HCs) and ensure communication with the extracellular environment.