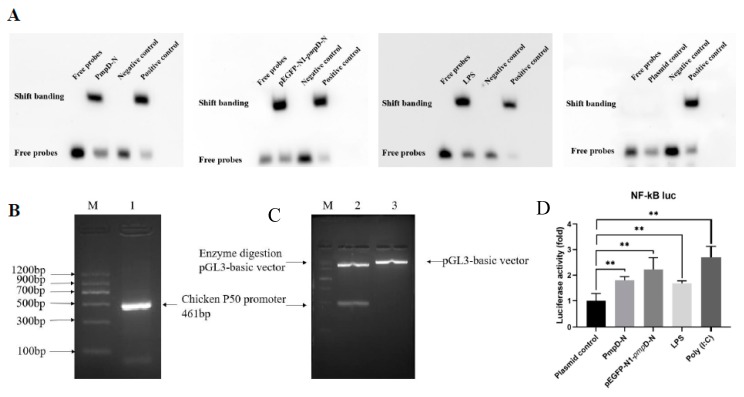
Figure 6.
Binding and activation of transcription factor NF-κB with promoter. (A) NF-κB protein–oligonucleotide complexing was performed using a LightShift chemiluminescent electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA). The transcription factor of NF-κB was bound to the promoter and showed band shifting post-treatment with rPmpD-N, pEGFP-N1-pmpD-N, or plasmid control. (B) Construction of chicken NF-κB transcription factor P50 promoters was identified to be positive by PCR. (C) The pGL3-basic-chp5-promoter was determined to be a 461 bp product by double enzyme digestion. M: Maker; 1: Chicken NF-κB transcription factor P50 promoters; 2: pGL3-basic-chp5-promoter; 3: pGL3-basic vector. (D) The NF-κB promoter activity was determined by luciferase activity in HD11 cells stimulated with exogenous or intracellular PmpD-N, LPS, or plasmid control for 6, 12, 24, and 48 h. Statistical analyses were performed with one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s post hoc multiple comparisons test. Statistically significant differences were evaluated at ** p < 0.01.