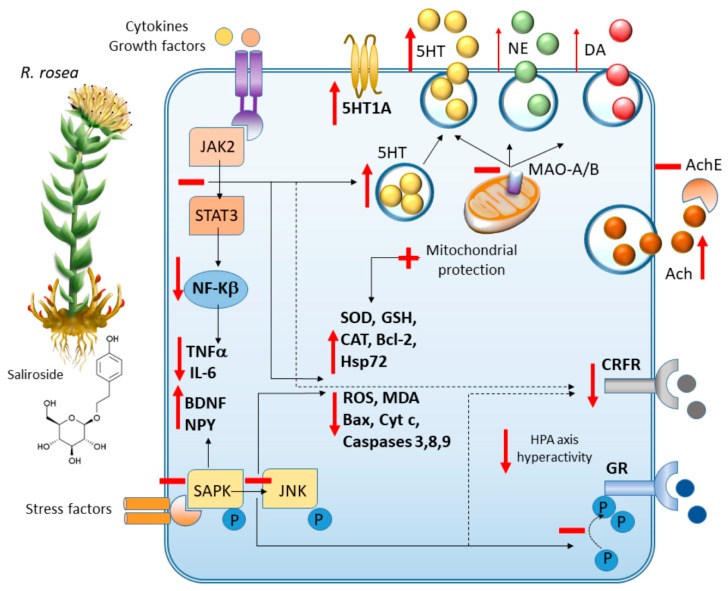
Figure 5.
R. rosea: molecular mechanisms underlying neuroprotective, cognitive enhancing and anxiolytic/antidepressant-like effects. By acting as MAO A/B inhibitor, R. rosea and its main bioactive ingredient (saliroside) induce monoamine, and mostly 5-HT release while potentiating 5-HT synthesis and the expression of 5-HT1A receptors. R. rosea also potentiates Ach release while acting as an Ach esterase (AchE) inhibitor. At the same time, R. rosea acts as a JAK/STAT and SAPK/JNK pathway inhibitor to promote the synthesis of neurotrophic factors along with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. JAK/STAT and SAPK/JNK pathway inhibition is also associated with R. rosea-induced downregulation of CRF receptors and inhibition of GR phosphorylation at crucial serine residues related to HPA axis activity.