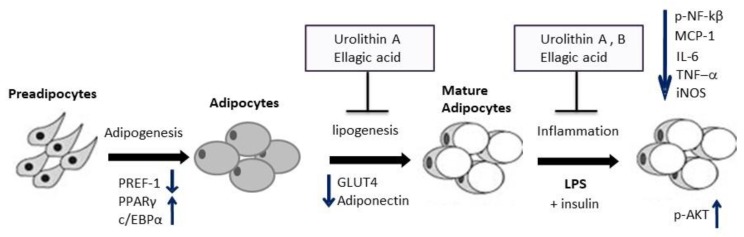
Figure 8.
Proposed model of modulation of lipogenesis and inflammation by ellagic acid and derived gut microbial metabolites urolithins A and B in adipocytes. Ellagic acid (EA) and urolithins A and B did not affect adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells, where PREF-1 decreased and PPARγ and c/EBPα increased for all treatments. During lipogenesis/lipolysis, only EA and urolithin A reduced fat accumulation in mature adipocytes attenuating GLUT4 gene expression and adiponectin. In LPS-challenged cells, EA and urolithins A and B differentially ameliorated inflammation through down-regulation of transcription factor p-NF-κB and pro-inflammatory genes while not affecting insulin sensitivity, depicted by an increase in protein expression of transcription factor p-AKT when exposed to insulin.