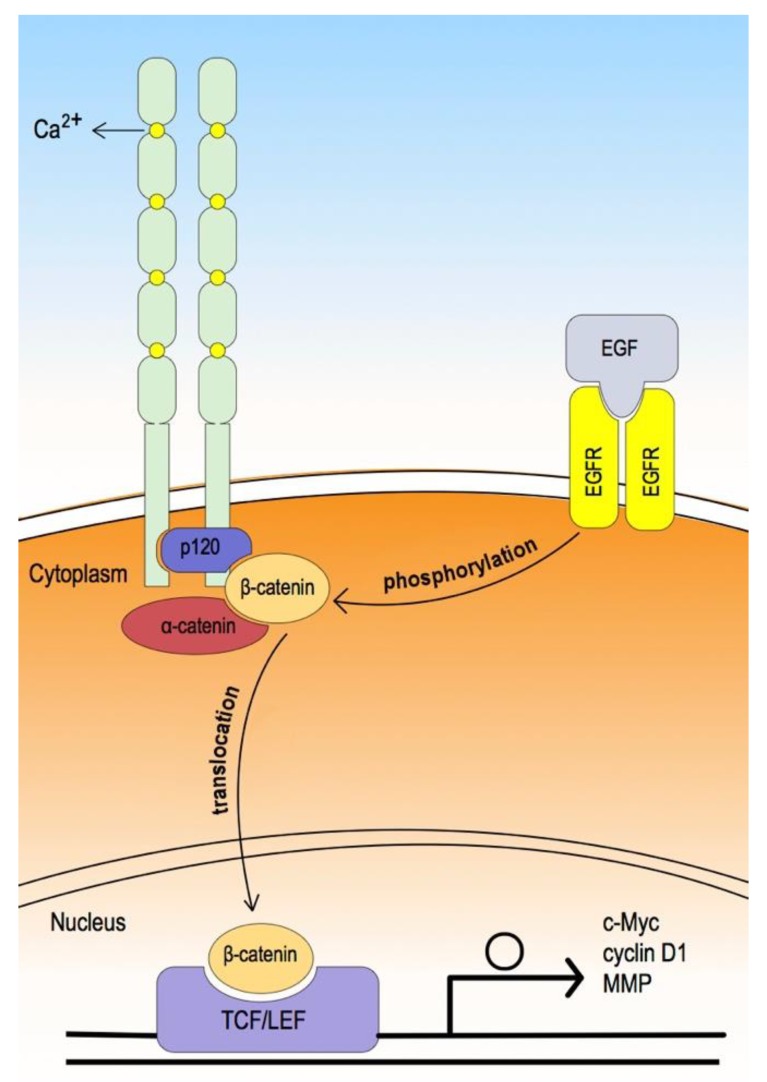
Figure 3.
The extracellular domain consists of five cadherin-type repeats bound together by calcium ions, forming a parallel cadherin dimer. In the cytoplasmic domain, the core universal-catenin complex consists of p120 catenin bound to the juxta-membrane region, and β-catenin, bound to the distal region, which in turn binds α-catenin; α-catenin then binds through actin or actin-binding proteins [55,56]. In contrast, while epidermal growth factor (EGF) binds to its receptor (EGFR) and activates EGFR, the phosphorylation of β-catenin and GSK-3β are induced. This leads to dissociation of β-catenin from the cadherin-catenin protein complex and translocation into the nucleus (phosphorylated GSK-3β also induces uncoupling of β-catenin from the destruction complex and translocation into the core through the canonical Wnt signaling pathway). Consequently, nuclear β-catenin binds with TCF/LEF and induces the transcription of the Wnt target gene, which affects the cell cycle, migration, and invasion [56,57].