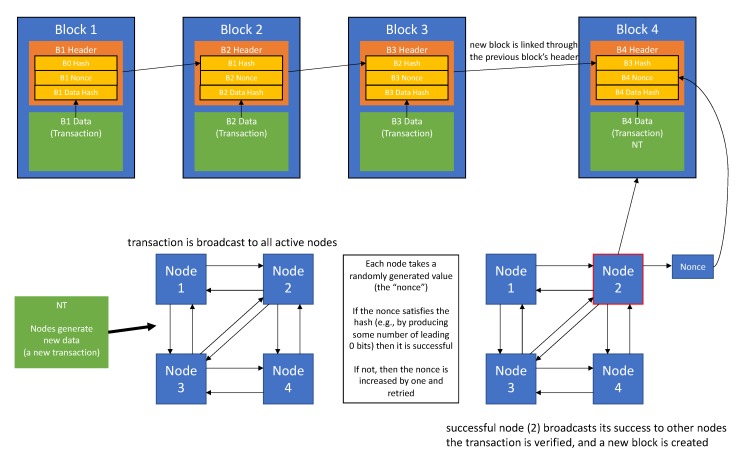
Figure 2.
Summary of basic blockchain methodology. When transactions are made that need to be stored in the chain. nodes compete to find a “nonce” that satisfies the hash-problem assigned to them. If the data is valid, the successful node creates a block, which is chained to the most recently created block in the longest chain.