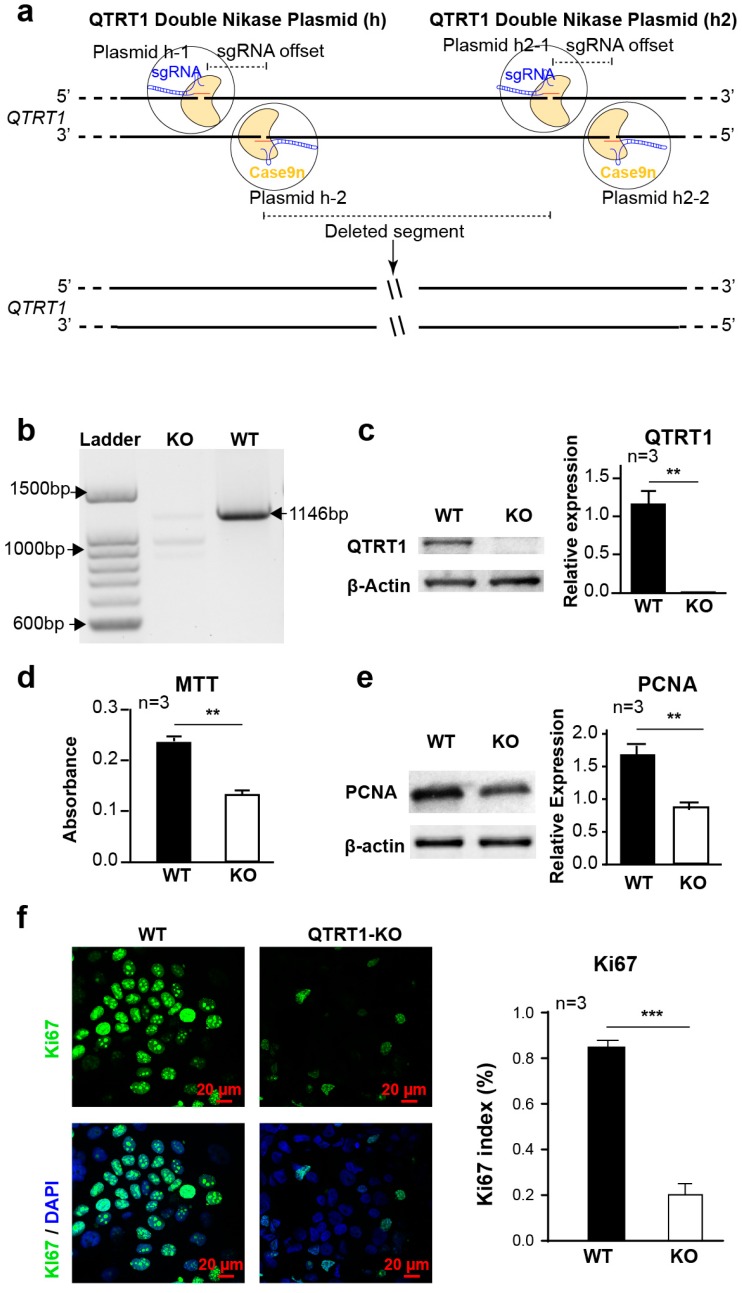
Figure 1.
Knockout of Q tRNA ribosyltransferase catalytic subunit 1 (QTRT1) suppressed MCF7 breast cancer cell proliferation. (a) Schematic illustration of double-stranded DNA breaks using a pair of Cas9 D10A nickases (Cas9n). (b) The deletion of QTRT1 in MCF7 cells was confirmed using PCR with primers specific for the QTRT1 gene. (c) Western blot analysis of wildtype (WT), QTRT1-knockout (KO) MCF7 cells generated using Double Nickase Plasmids after treating for 72 h. Mean ± SD, n = 3; ** p-value < 0.01, two-tailed Welch’s t-test. (d) MTT assay to show cell proliferation of WT and QTRT1-KO MCF7 conducted at 48 h after seeding the same number of cells. Mean ± SD, n = 3; ** p-value < 0.01, two-tailed Welch’s t-test. (e,f) Cell proliferation markers of PCNA (proliferating cell nuclear antigen) and Ki67 in WT and QTRT1-KO MCF7 cells were detected using Western blot (E) and immunofluorescence staining (F), respectively. Immunofluorescence staining of Ki67 and DAPI were performed in the cells, and Ki67 index (Ki67 stained cells/total cells) was calculated. Mean ± SD, n = 3; ** p-value < 0.01, *** p-value < 0.001, two-tailed Welch’s t-test.