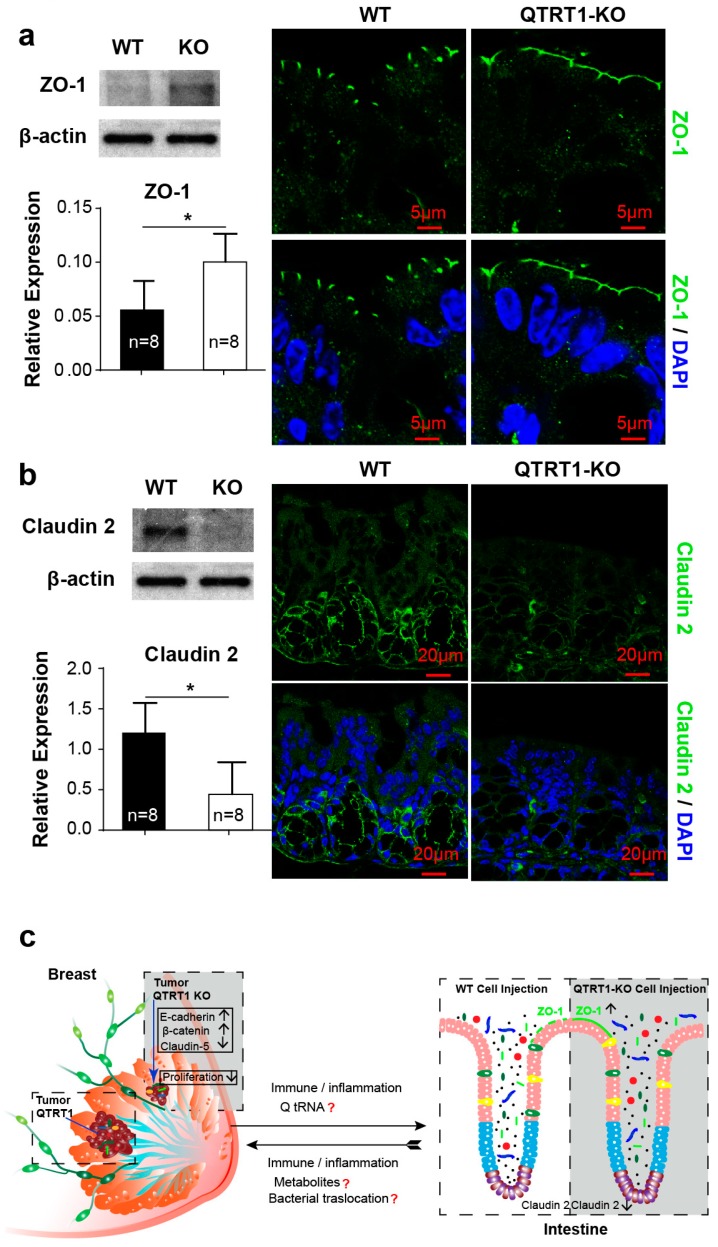
Figure 6.
Altered tight junction proteins in the colon of a nude mouse model. Western blot analysis and immunofluorescence staining of ZO-1 (a) and claudin-2 (b) were performed on the colons of the nude mice injected with WT and QTRT1-KO MCF7 breast cancer cells. Proteins and DNA were stained with rabbit monoclonal anti-ZO-1/ mouse monoclonal anti-claudin-2 and anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 488 antibody, and DAPI, respectively. Scale bar is 5 µm in (a) and 20 µm in (b). The graphs show the relative expression of the target proteins detected by Western blot. Mean ± SD, n = 8; * p-value < 0.05, two-tailed Welch’s t-test. (c) The working model of QTRT1/Q-tRNA modification regulating gut-tumor-microbiome axis in breast cancer. Knockout of QTRT1 inhibited beast tumor proliferation and growth by altering the expressions of claudin-5, E-cadherin, and β-catenin in breast and changed the microenvironment of tumors. Meanwhile, the altered expression of intestinal junction proteins (claudin-2 and ZO-1) and altered bacterial community were found in the colon of mice with breast cancer cells. Microbiome-dependent tRNA Q-modifications regulate tumor growth and recruit microbiome to breast tumors. It is still unknown what the roles are of Q tRNA and metabolites in the process, and whether there is bacterial translocation from the intestine to the breast.