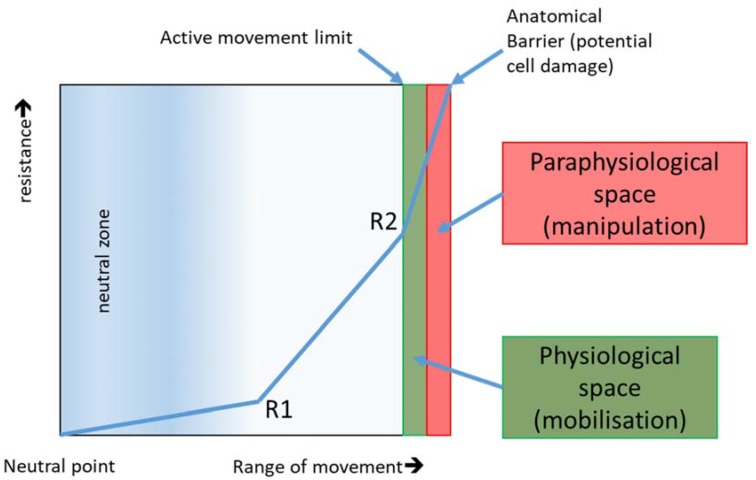
Figure 5.
Behaviour of resistance depending on the extent of movement in joints and connective tissue. R1 represents the first and R2 represents the second remarkable increase in connective tissue resistance. Depending on the intensity of the manual degree classification (dosage), therapists treat passively more or less into physiological space. The paraphysiological space is only achieved by impulse mobilisation. If the anatomical barrier is crossed, cell damage occurs (lesion) and reacts with an inflammatory reaction. This anatomical barrier is important in post-traumatic and postoperative conditions due to adhesions and water soluble crosslinks to the front postponed. Especially in the proliferation phase, it can quickly lead to an overdose. The microtraumatic injuries trigger new inflammatory phases, which result in increased restriction of movement and restriction [25] (source: own illustration).