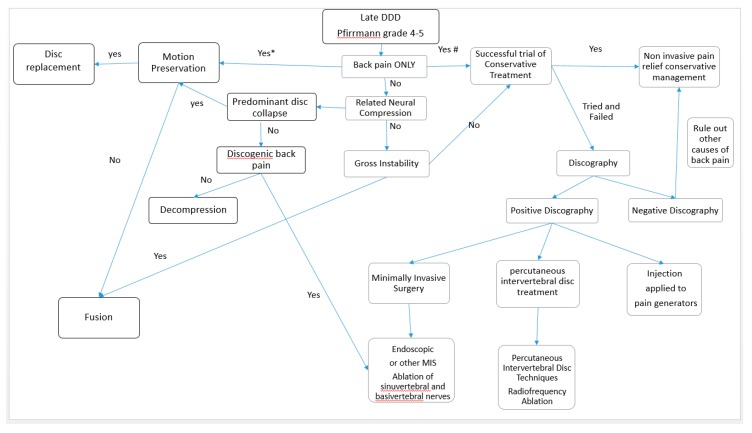
Figure 4.
Decision flow chart in clinical practice for patients with late degenerative disc disease, Pfirrmann grade 4–5. We assess for any related pure axial back pain, neural compression, and instability. If there is no neural compression or instability and only pure axial back pain, the patient should be offered a trial of conservative noninvasive treatment as a first line of treatment (#). It is controversial regarding total disc replacement and fusion surgery as a first line of definitive treatment for back pain. Both are invasive and irreversible procedures; hence, they should be considered as a last option in pure axial back pain even in advanced degenerative disc disease (*). If conservative management fails, discography should be considered. In a negative discography, we need to rule out other causes of back pain and continue conservative management. In a positive discography with pure axial back pain in advanced disc degeneration, the less invasive option of injection to pain generators, such as epidural steroid injection, percutaneous epidural neurolysis, peri-radicular injection, and facet joint blocks, can be considered for temporal relief of symptoms. Clinicians can consider other more definitive palliative management, such as radiofrequency ablation, which can be applied by minimally invasive techniques, such as endoscopic radiofrequency ablation of the sinuvertebral, basivertebral nerve, and disc, or fluoroscopic-guided percutaneous intervertebral disc treatment, such as radiofrequency ablation of the disc. Neural compression without instability or disc collapse can be treated with decompression only for patients without discogenic back pain. While for patients with discogenic back pain and neural compression, decompression surgery with additional endoscopic or other methods of treatment of the sinuvertebral and basivertebral nerve can be done [12]. Total disc replacement is done when there is disc collapse with the intention to preserve motion; fusion is done when there is disc collapse with the intension of rigid fusion. If there is any symptomatic gross instability, fusion surgery should be considered.