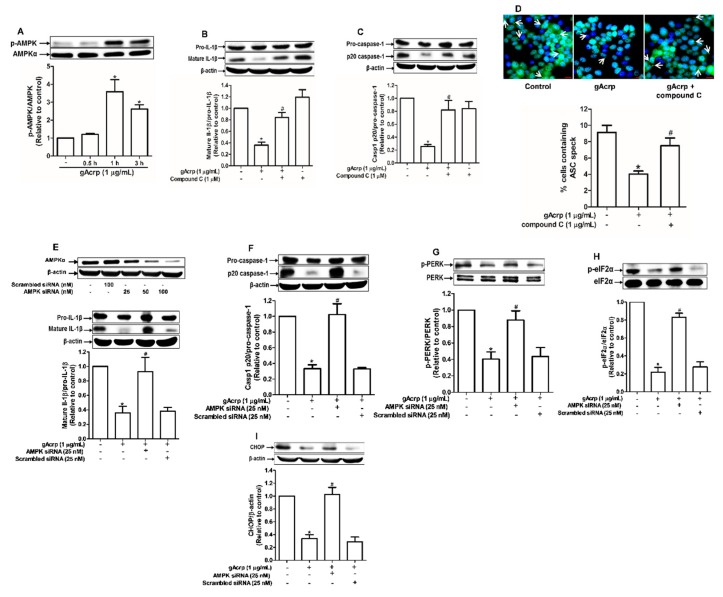
Figure 3.
Crucial role of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling in the modulation of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and inflammasomes by globular adiponectin. (A) MCF-7 cells were treated with gAcrp (1 µg/mL) for the indicated time periods. The expression levels of AMPKα were measured by Western blot analysis. (B,C) MCF-7 cells were pretreated with compound C (1 µM), a pharmacological inhibitor of AMPK, for 1h followed by further treatment with gAcrp (1 µg/mL) for additional 24 h. Total protein lysates were prepared and used for immunoblotting analysis for the measurement of interleukin-1β (IL-1β) (B) and Caspase-1 (C). (D) After pretreatment with compound C for 1 h, MCF-7 cells were incubated with gAcrp (1 µg/mL) for additional 1 h and further incubated with antibodies for specific ASC (green) and DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 5µm. (E–I) MCF-7 cells were transfected with siRNA targeting AMPKα or control scrambled siRNA. Gene silencing efficiency of AMPKαwas monitored by Western blot analysis (Upper panel in Figure 3E). After transient gene silencing of AMPKα, cells were treated with gAcrp for 24h (E,F) or 1 h (G–I). IL-1β (E), Caspase-1 (F), protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK) (G), Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2A (eIF2α) (H), and C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) (I) expression levels were determined by Western blot analysis. Values are presented as the fold change compared with the control cells and are expressed as mean± standard error of mean (SEM), n= 3. * denotes p < 0.05 compared to control cells, # denotes p < 0.05 compared with the cells treated with globular adiponectin but not pretreated with compound C (B,C) or not transfected with siRNA (E–I).