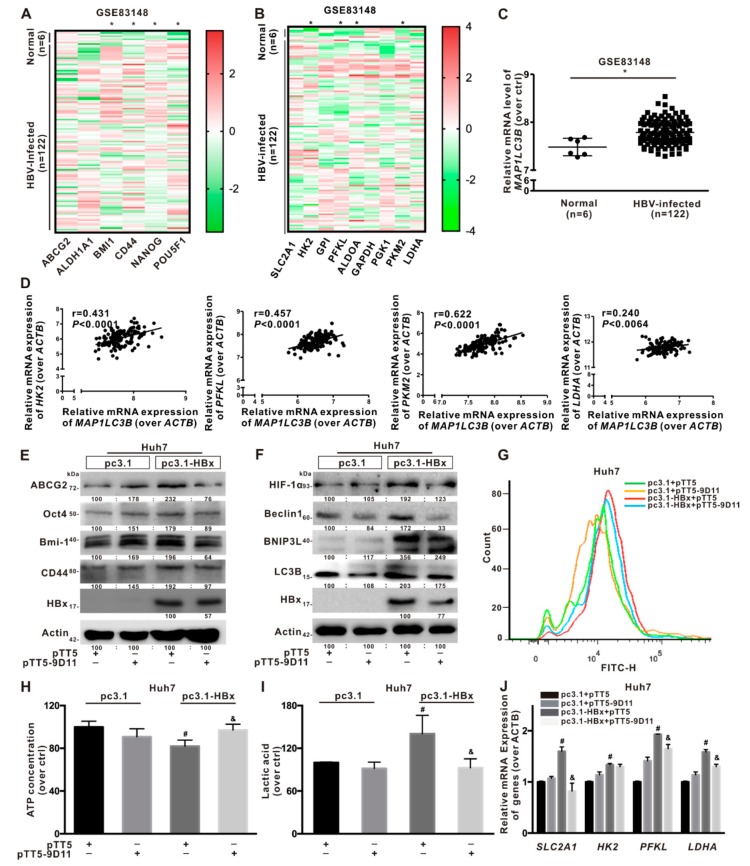
Figure 8.
Anti-HBx targeting intervention to intracellular HBx inhibited the hepatocarcinogenesis associated with BNIP3L-dependent mitophagy. (A–D) The relative mRNA levels of indicated genes were obtained from NCBI, GEO database (GSE83148). The clinical cohort samples were derived from HBV-infected liver tissues (n = 122) and normal liver tissues (n = 6). The heat-map of the relative mRNA levels of cancer stemness-related genes (A) and glycolysis-related metabolism genes (B), the relative mRNA levels of MAP1LC3B gene (C), and the linear correlation of MAP1LC3B with glycolysis-related metabolism genes (D) were shown. (E–J) Huh7 cells without or with HBx-expressing were transiently transfected with pcDNA3.1 or pcDNA3.1-HBx (1 μg/mL), and then transiently transfected with pTT5 or pTT5-9D11 plasmids (200 ng/mL) for 8 h, and cultured for another 24 h. pTT5-9D11 plasmids encoded anti-HBx, a monoclonal antibody (mcAb), directed against intracellular HBx. (E) The expression levels of cancer stemness-related proteins. (F) The expression levels of BNIP3L-dependent mitophagy-related proteins. The gray value of band was assessed by image-pro plus 6.0. The relative expression level was shown. (G) Glucose transport activity was evaluated by FCM. The levels of the intracellular ATP content (H), the extracellular lactic acid secretion (I), and the mRNA levels of glycolysis-related genes (J) were detected. The target gene transcription was normalized to ACTB. * P < 0.05 as compared with normal liver tissues group. # P < 0.05 as compared with Huh7 group. & P < 0.05 as compared with HBx-expressing Huh7 group. pc3.1: pcDNA3.1 transfection without HBx-expressing. pc3.1-HBx: pcDNA3.1-HBx transfection with HBx-expressing.