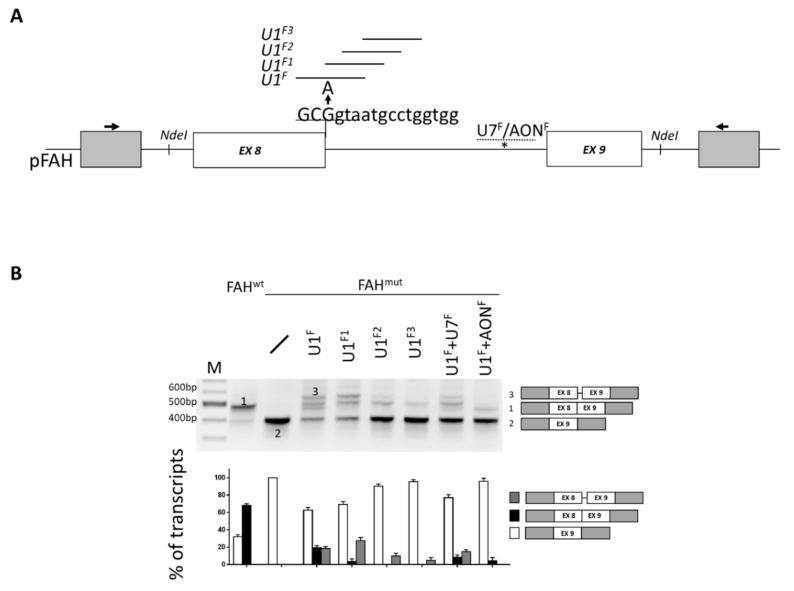
Figure 1.
The mouse FAH c.706G>A mutation can be rescued by engineered U1snRNAs. (A) Schematic representation of the mouse FAH minigene with exonic and intronic sequences represented by boxes and lines, respectively (not in scale). Exonic and intronic nucleotides are indicated in upper and lower cases respectively. The nucleotide change (G>A) leading to the FAH deficiency in FAH5961SB mice is indicated (arrow). The targeting regions of the engineered U1snRNAs or the U7snRNA/AONF are reported as continuous and dotted lines, respectively. The cryptic 5′ss at position +63 in intron 8 is indicated by an asterisk. (B) FAH splicing patterns in Hepa1-6 cells transiently transfected with the wild-type (FAHwt) or mutated (FAHmut) minigenes, alone or in combination with U1/U7snRNA or the AONF. The schematic representation of the transcripts (numbers 1 to 3, with exons not in scale) is reported on the right. Amplified products were separated on 2% agarose gel. M, 100 bp molecular weight marker. The lower panel reports the evaluation of amplicons by denaturing capillary electrophoresis (see Figure S1A). Histograms report the relative percentage of each transcript expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD).