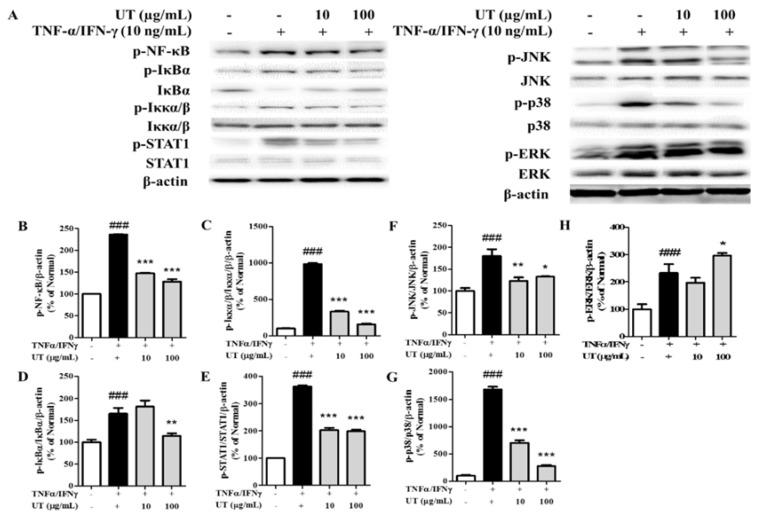
Figure 3.
Effect of UT on NF-κB/STAT1 and MAPK signaling pathways in TNF-α/IFN-γ-stimulated HaCaT cells. (A) NF-κB, IκBα, Iκκα/β, STAT1, JNK, p38, and ERK phosphorylation was assessed by western blot analysis. Band intensities for p-NF-κB (B), p-Iκκα/β (C), p-IκBα (D), p-STAT1 (E), p-JNK (F), p-p38 (G), and p-ERK (H) were quantified by densitometry, normalized to the level of β-actin, and calculated as a percentage of the basal response. Values shown are the mean ± SD. # Significant differences from group 1 and the TNF-α/IFN-γ-induced group (# P < 0.05; ## P < 0.01; ### P < 0.001). * Significant differences from the TNF-α/IFN-γ-induced group and groups 3, 4, and 5 (* P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001). UT, Urtica thunbergiana; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; STAT1, signal transducer, and activator of transcription 1; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IFN-γ, interferon-gamma; IκBα, inhibitor of kappa B alpha; Iκκα/β, inhibitor of kappa kinase alpha; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; ERK, extracellular-signal-regulated kinase; SD, standard deviation.