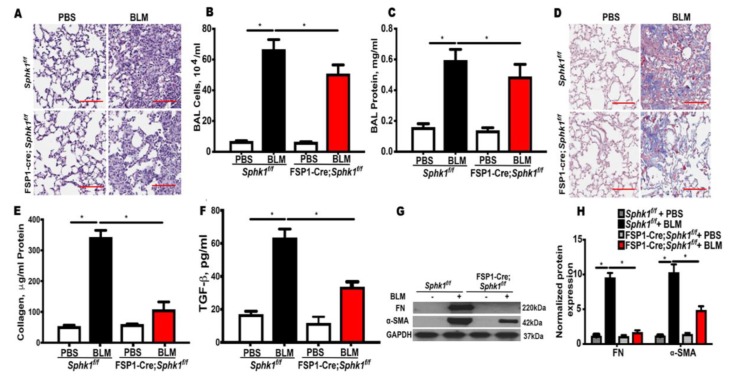
Figure 1.
Deletion of Sphk1 in fibroblasts attenuates bleomycin induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Sphk1flox/flox and Sphk1flox/flox: FSP1Cre+ mice (male, 8 weeks) in C57BL/6 background receiving BLM (2 U/kg in 50 µL phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) solution) or PBS intratracheally were sacrificed at day 21 post-challenge. (A) Representative H&E images of lung sections from Sphk1flox/flox and FB-Sphk1KO mice with/without BLM challenge. Original magnification, ×10; Scale bar: 200 µm. (B) Total cell number in the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid. (C) Total protein levels in the BAL fluid. (D) Representative Masson’s trichrome stains of the lung tissue sections obtained from Sphk1flox/flox and FB-Sphk1KO mice with/without BLM challenge. The histology images show original magnification, ×4; Scale bar: 1 mm. (E) Relative quantitative data for acid soluble collagen in lung tissue. (F) Relative transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) levels in the BAL fluids. (G,H) Protein levels of fibronectin (FN) and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) in lung tissue from Sphk1flox/flox and FB-Sphk1KO mice with/without BLM challenge. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05; n = 4–6 per group.