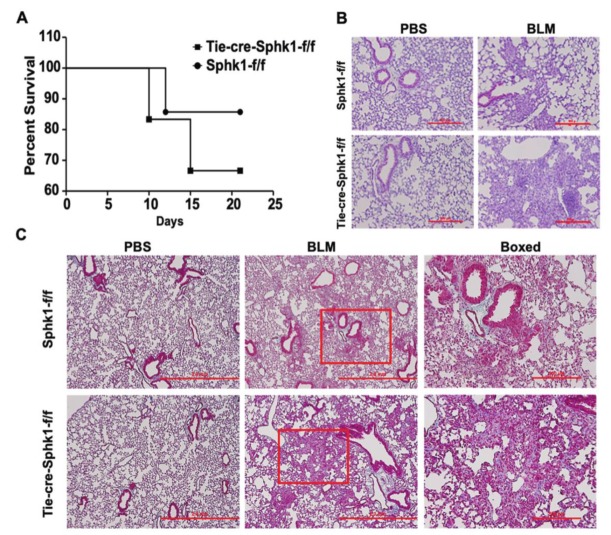
Figure 3.
Deletion of Sphk1 in endothelial cells does not protect mice from bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. Sphk1flox/flox and Sphk1flox/flox: Tie-Cre+ mice (male, 8 weeks) in C57BL/6 background receiving bleomycin (BLM) (2 U/kg in 50 µl PBS) or PBS intratracheally were sacrificed at day 21 post-challenge. Lungs were removed, embedded in paraffin, and cut into 5 µm sections for staining. (A) Survival of Sphk1flox/flox and Tie-Sphk1KO mice challenged with or without BLM challenge. (B) Representative H&E photomicrographs of lung sections obtained from Sphk1flox/flox and Tie-Sphk1KO mice with/without BLM challenge. (C) Masson’s trichrome staining for collagen deposition. Representative images of Trichrome staining of lung sections obtained from Sphk1flox/flox and Tie-Sphk1KO mice with/without BLM challenge. The area within the red box is zoomed and showed in the boxed panel. Scale bar: 500 µm (Figure B); 2mm and boxed ones 500 µm (Figure C). n = 4–6 per group.