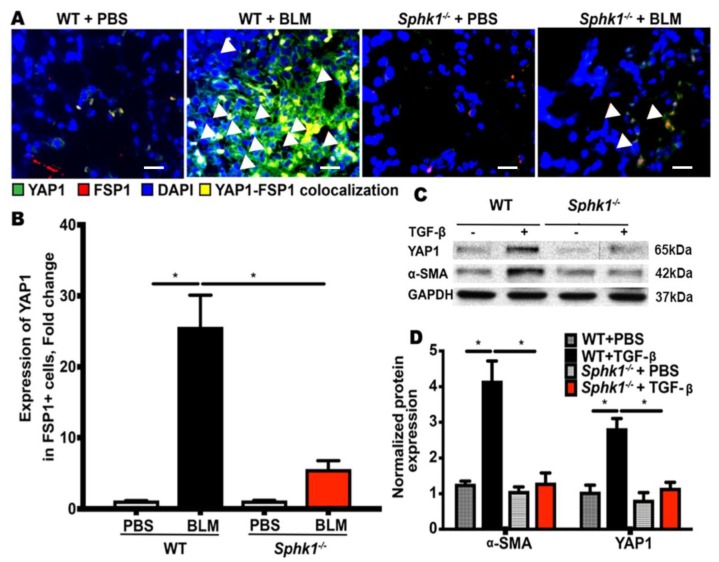
Figure 4.
Genetic deletion of Sphk1 in fibroblasts reduces bleomycin- and TGF-β-induced Hippo/Yes-associated protein (YAP) 1 expression. (A,B) Sphk1flox/flox and Sphk1flox/flox: FSP1Cre+ mice (male, 8 weeks) in C57BL/6 background receiving bleomycin (BLM) (2 U/kg in 50 µL PBS) or PBS intratracheally were sacrificed at day 21 post-challenge. Lungs were removed, embedded in paraffin, and cut into 5 µm sections for immunofluorescence staining for FSP1 and YAP1. Shown is a representative micrograph of co-localization of FSP1 and YAP1. BLM increased co-localization (yellow) of FSP1 (green) and YAP1 (red) in lung fibroblasts of Sphk1flox/flox mice, but not Sphk1-deficient mice. The white triangular arrows highlights the YAP1-FSP1 colocalized areas in the image. (C,D) Lung fibroblasts isolated from Sphk1flox/flox and Sphk1-deficient mice were incubated with transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) (5 ng/mL) for 48 h and expressions of fibronectin (FN), α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), and YAP1 were determined by Western blotting with glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) as loading control. TGF-β enhanced YAP1 and α-SMA expression in wild type (WT)mouse lung fibroblasts (MLFs), which was reduced in Sphk1-deficient cells. * p < 0.05, significantly different from WT cells treated with vehicle, and MLF-deficient in Sphk1. n = 4–6 per group. Scale bar: 20 µm.