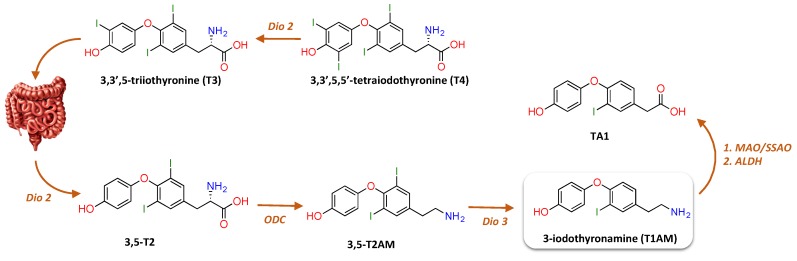
Figure 2.
Proposed metabolic pathway to the production of T1AM from T4 in rat gut preparation. As mentioned in the review’s text, in a rat gut preparation it was found that T4 or T3 administered exogenously was first deiodinated by type II deiodinase (Dio2) to form 3,5-T2, which underwent decarboxylation by ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) to generate 3,5-T2AM, followed by Dio3-catalysed deiodination to yield T1AM [31]. Notably, once inside cells, T1AM is rapidly metabolized by ubiquitous enzymes, including monoamine oxidase (MAO), semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase (SSAO), and aldehyde dehydrogenase (ADLH), producing 3-iodothyroacetic acid (TA1).