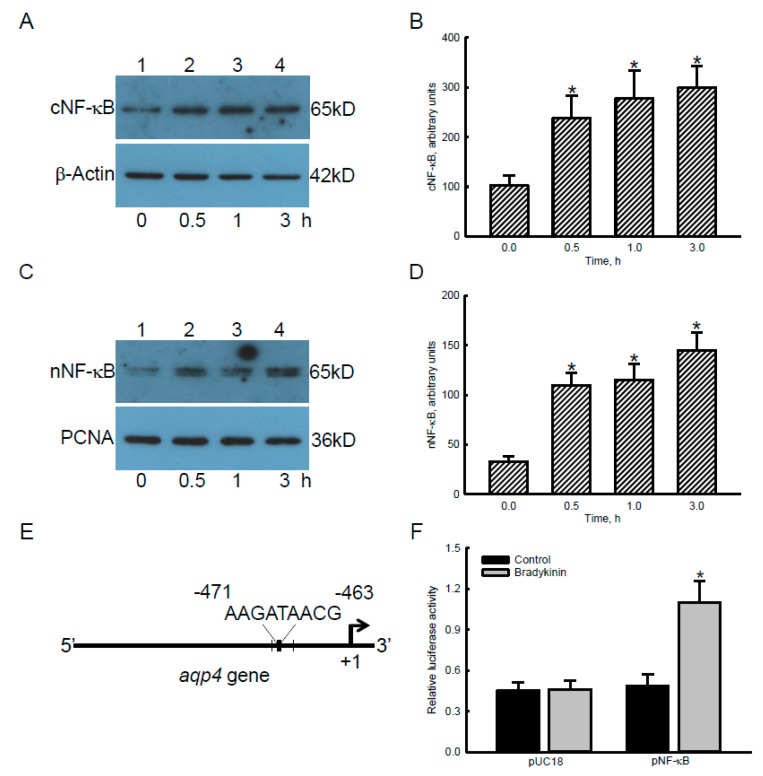
Figure 4.
Effects of bradykinin on levels, translocation, and transactivation activity of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) in human malignant glioblastoma cells. Human U87 MG glioblastoma cells were treated with 100 nM bradykinin for 0.5, 1, and 3 h. Levels of cytosolic (c) and nuclear (n) NF-κB were immunodetected (A,C, top panels). Amounts of β-actin and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) were analyzed as internal controls for the cytosolic and nuclear proteins, respectively (bottom panels). These protein bands were quantified and statistically analyzed (B,D). A schematic diagram indicates the NF-κB-specific DNA binding element (−463 to −471) in the 5’-promoter region of the aqp4 gene (E). The NF-κB luciferase reporter plasmids (pNF-κB) and pUC18 control plasmids (pUC18) were transfected into human U87 MG cells. Transactivation activity of NF-κB was assayed with a reporter gene assay (F). Each value represents the mean ± standard deviation (SD), n = 9. An asterisk (*) indicates that a value significantly (p < 0.05) differed from the respective control. Representative immunoblots are shown.