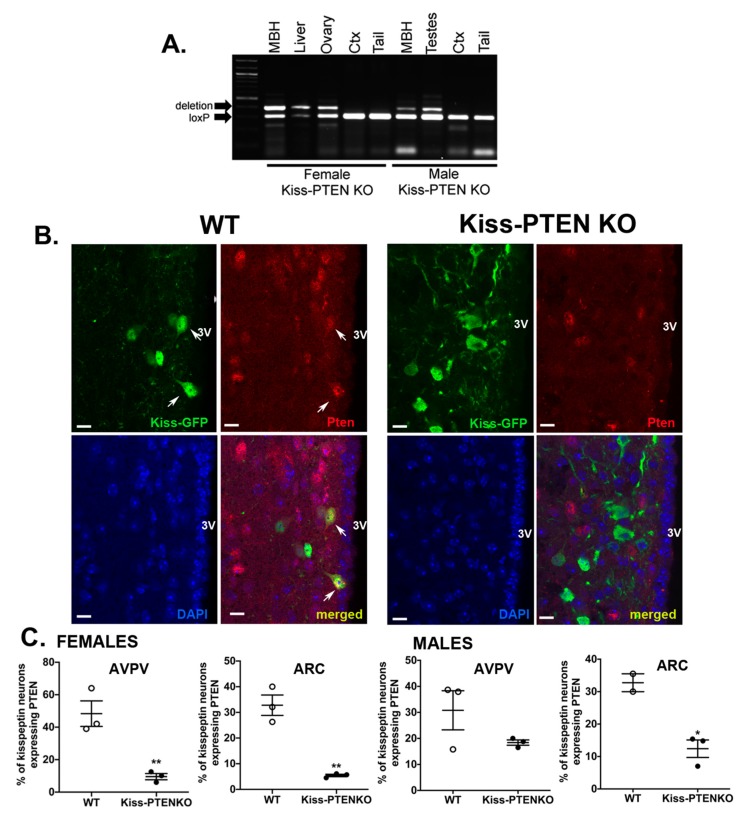
Figure 1.
Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) deletion is restricted to kisspeptin-expressing tissues and neurons in Kiss-PTEN KO mice. (A) Representative PCR analyses showing deletion of Pten exon 5 (404 bp product) in the mediobasal hypothalamus (MBH), liver, and gonads, whereas no deletion is observed in the cortex (Ctx) or tail (floxed 335 bp band only). Genomic DNA was isolated from indicated tissues from female and male Kiss-PTEN KO (Kiss-Cre+/PTENflx/flx) mice. (B) Representative images of double-immunofluorescent labeling of PTEN and GFP in Kiss-PTEN KO/R26-YFP mice show that the loss of PTEN expression is restricted to Kiss-YFP+ neurons. White arrows indicate double-labeled kisspeptin neurons. Scale bar = 10 μm. 3V, third ventricle. (C) The percentage of Kiss-YFP+ cells co-expressing PTEN in both the anteroventral periventricular nucleus (AVPV) and arcuate nucleus (ARC) is lower in Kiss-PTENKO/R26-YFP animals (n = 2–3/genotype and sex). Values are means ± SEM. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.