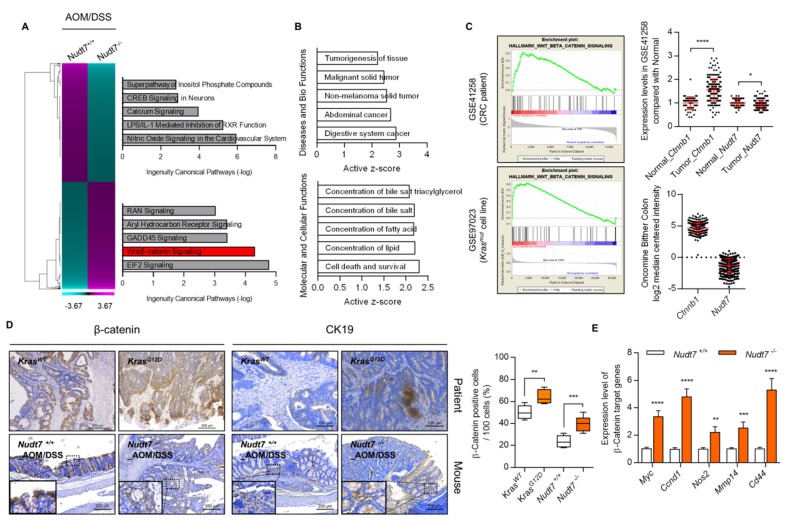
Figure 5.
Suppression of Nudt7 increases β-catenin signaling. (A) Canonical pathway was analyzed using IPA software (Qiagen, Redwood, CA, USA) from microarray data of Nudt7+/+ and Nudt7−/− colons treated with AOM/DSS. (B) Active z-score of disease and biological functions or molecular and cellular functions were analyzed using IPA software. (C) GSEA analysis using GEO datasets (CRC patient biopsy dataset, GSE41258 and KrasG12D mutation CRC cell line dataset, GSE97023) and expression levels of Nudt7 and Ctnnb1. (D) Immunohistochemical staining with β-catenin and CK19 and positive cell count in Nudt7+/+ and Nudt7−/− mice treated with AOM/DSS (n = 4; 100× magnification; scale bars: 200 μm) and KrasG12D-derived CRC patient (n = 4; β-catenin, 100× magnification, scale bars: 200 μm; CK19, 200× magnification, scale bars: 100 μm) and positive cells were counted for every 100 cells in 3 different fields. CK19 was used as a marker for epithelial tissue. Results are representative of at least 3 independent experiments. The dotted line boxes were enlarged in the bottom left corner of each image. (E) Transcriptional levels of β-catenin target genes and presented as the fold change compared with Nudt7−/− mice. Rn18s was used as an endogenous control. Results are representative of at least 3 independent experiments. Values are means + SD. An unpaired Student’s t-test was used for statistical analysis. * p ≤ 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001.