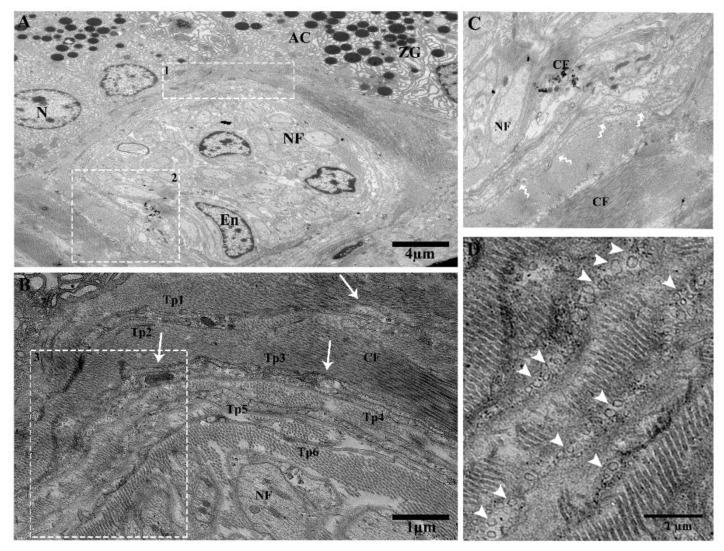
Figure 7.
Large duct attached with lobules through the connective tissue in between the gland cells. Tps surround the ductus and form triangular structures and shading vesicles in the connective tissue. (A) Telopodes establishing a triangular structure “trio” adjacent to the acinar cells and collagen fibers, nerve fibers, and telopodes showing nano-contacts. Square-marked areas 1 and 2 in (A) are enlarged in (B,C) respectively. (B) Tp1, Tp2, Tp3, and Tp4 have gap junctions, and there are close connections between Tp5 and Tp6. The podoms contain mitochondria and caveolae (white arrows). (C) In the vicinity of collagen fibers, nerve fiber Tps junctions (podoms–podoms) and segments (bent arrows) can be seen. The square-marked area 3 in (B) is enlarged in (D), where numerous shading vesicles (arrowheads) in the connective tissue, along with collagen fibers, at the ending point of Tp1, Tp2, Tp3, Tp4, Tp5, and Tp6 are often captured, which suggests a transfer of information between telopodes and adjacent cells. Tp, telopodes; CF, collagen fibers; NF, nerve fiber; En, endothelial cells; AC, acinus; ZG, zymogen granules. Scale bar =4 µm in (A); scale bar = 1 µm in (B,D).