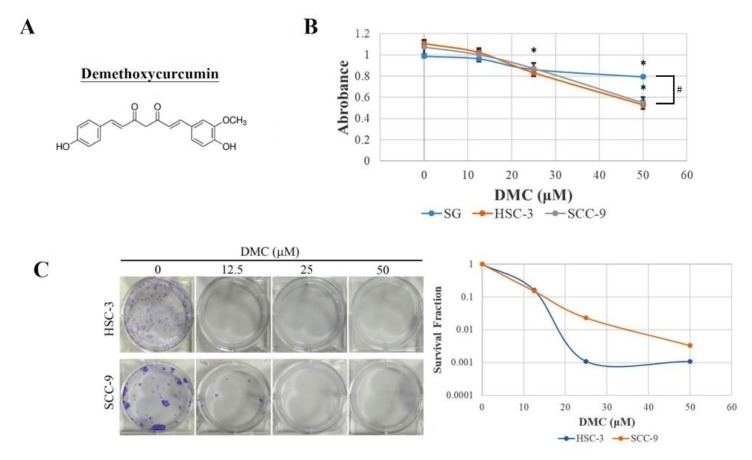
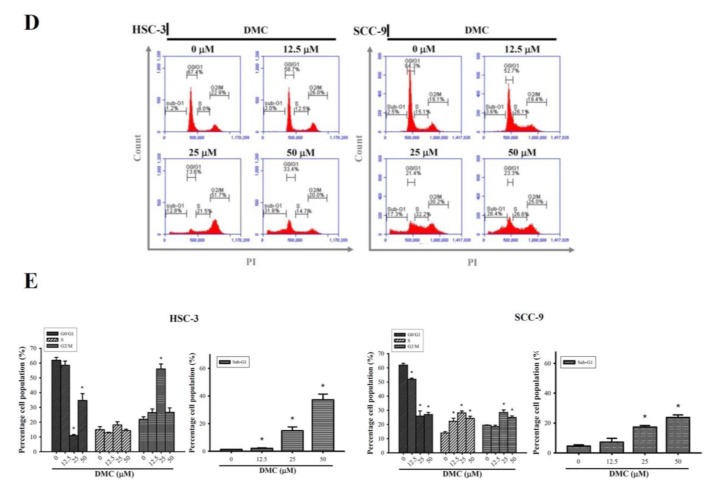
Figure 1.
Demethoxycurcumin (DMC) inhibits the proliferation and colony formation via inducing G2/M phase arrest in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cells. (A) The chemical structure of DMC. (B) Two OSCC cell lines, SCC-9 and HSC-3, and one normal gingival epithelial cell line, SG, were treated with indicated concentrations of DMC (12.5, 25, and 50 μM) or DMSO (vehicle control) for 24 h, and a thiazolyl blue tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay was performed to determine the cell viability. * p < 0.05, compared to the DMSO-treated group. # p < 0.05, compared to the OSCC cells. (C) After 24 h treatment of vehicle or DMC (12.5–50 μM) with OSCC cells, the medium was changed to remove DMC, and SCC-9 and HSC-3 cells were respectively maintained in fresh medium for 18 and 7 days to determine the long-term death-inducing effects of DMC. Representative photomicrographs were shown in the left panel. Data was given semi-logarithmically as a survival fraction/DMC dose plot. (D) After 24 h treatment of vehicle or DMC (12.5–50 μM) with SCC-9 and HSC-3 cells, the cell-cycle phase distribution and cell death in the sub-G1 phase were analyzed by FACS after propidium iodide (PI) staining. (E) Diagrams summarize cell-cycle results.