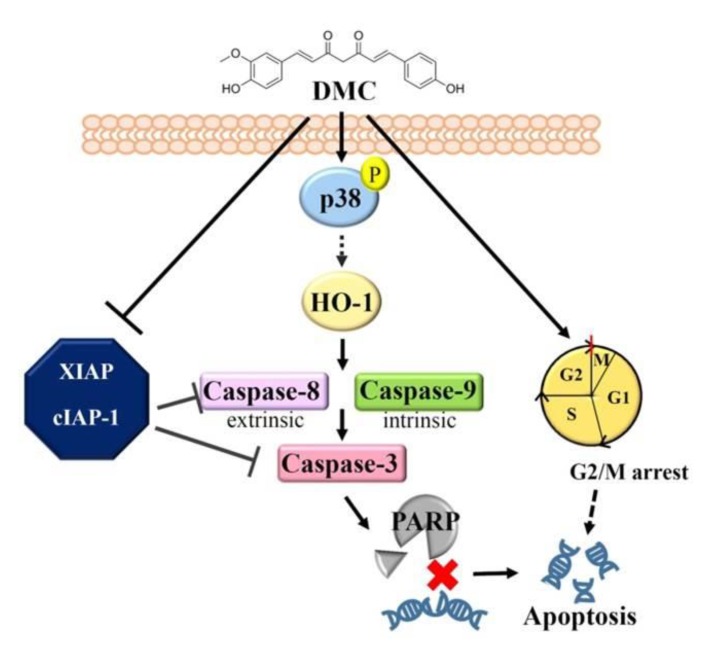
Figure 6.
A working model shows the molecular mechanism underlying the ability of demethoxycurcumin (DMC) to suppress the growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cells. The antiproliferative activity of DMC against OSCC cells derived from primary and metastatic sites was attributed to inhibition of cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 1 (cIAP1)/X-chromosome-linked IAP (XIAP) expression and activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-heme oxygenase (HO)-1 axis, with the ultimate induction of apoptotic cell death. Moreover, the induction of G2/M arrest might be another cause for the DMC-induced apoptotic cell death in OSCC cells.