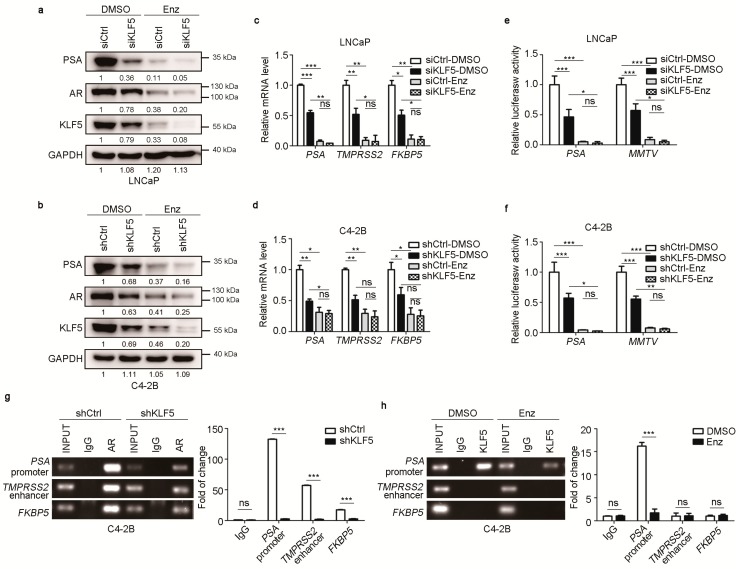
Figure 2.
KLF5 is crucial for the transcriptional activity of AR in PCa cells. (a–d) Knockdown of KLF5 reduced the expression of AR transcriptional target genes PSA, TMPRSS2, and FKBP5. Gene expression was detected for protein by western blotting (a, b) and real-time qPCR for mRNA (c, d). LNCaP (a, c) and C4-2B (b, d) cells in full medium were transfected with siRNAs (a, c) or infected with shRNA lentiviruses (b, d) to silence KLF5. One group of cells were treated with enzalutamide (10 µM, 24 h) to inhibit AR function, which served as a control. siCtrl and shCtrl are control siRNA and shRNA respectively. (e,f) Knockdown of KLF5 reduced the activities of two androgen-responsive promoters, PSA and MMTV, in the same cells with the same treatments as in panels a-d, except that the PSA– or MMTV–luciferase reporter plasmid and Renilla-luciferase reporter plasmid were transfected for 24 h before enzalutamide treatment. (g) Binding of AR to the promoters of PSA and FKBP5 and the enhancer of TMPRSS2 was detected after the knockdown of KLF5 in C4-2B cells, as detected by ChIP and regular PCR (left) or real-time qPCR (right). Cells were infected with lentiviruses expressing shRNAs against KLF5 (shKLF5) or control (shCtrl) to knock down KLF5. (h) KLF5 binds to the promoter of PSA but not the promoter of FKBP5 or the enhancer of TMPRSS2 in C4-2B cells in full medium, as detected by ChIP and regular PCR (left) or real-time qPCR (right). Cells were treated with enzalutamide (10 µM, 24 h), with DMSO as a control. ns, not significant; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.