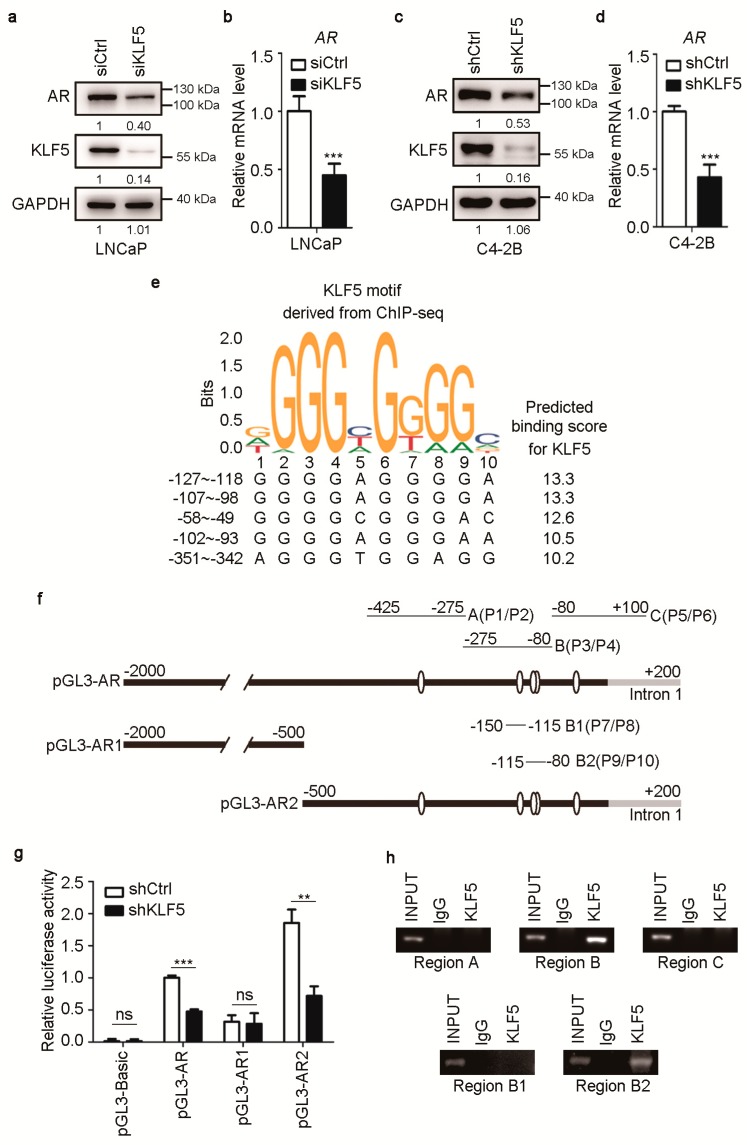
Figure 3.
KLF5 is required for the transcription of AR in PCa cells. (a–d) Knockdown of KLF5 decreased AR expression at both protein (a, c) and RNA (b, d) levels in LNCaP (a-b) and C4-2B cells (c–d). Cells were cultured in complete media for 24 h and transfected with siRNAs for 48 h in LNCaP cells or infected with lentiviruses expressing shRNA targeting KLF5 (shKLF5) in C4-2B cells. Western blotting and real-time qPCR were performed to detect protein and mRNA respectively. (e) The AR promoter contains multiple potential KLF5 binding sites, as predicted by aligning the 2-Kb immediate promoter sequence of AR to the consensus KLF5 binding sequence (top) defined in the JASPAR database. Location of these sequences relative to the transcription initiation site (+1) is shown at left. (f) Schematic of the AR promoter region (−2000 to +200) with the locations of predicted KLF5 binding sites (empty oval) and primers used for PCR amplification of 5 regions (A, B, C, B1, B2) of the AR promoter spanning the potential binding sites. (g) Knockdown of KLF5 decreased AR promoter activity in C4-2B cells, as detected by the luciferase activity assay. The pGL3 vector was used to express full-length AR promoter (g, pGL3-AR, from −2000 to +200) and two shorter AR promoter fragments (pGL3-AR-1, −2000 to −500; pGL3-AR-2, −500 to +200), with their luciferase readings normalized by that of the pGL3-Basic vector control. (h) Detection of KLF5-bound AR promoter DNA in C4-2B cells using ChIP and PCR. ns, not significant; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.