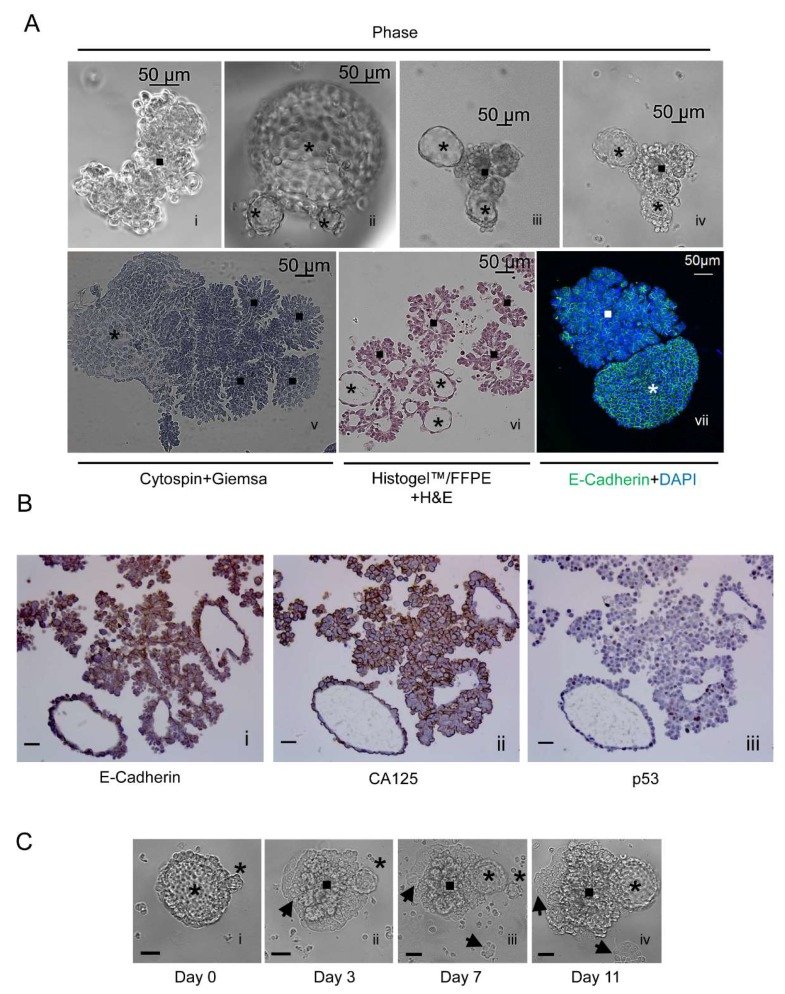
Figure 3.
(A) [i–iv] Phase-contrast images of irregular and spheroidal PEO6 multicellular structures; [v] cytospin and Giemsa staining; [vi] H&E staining of a 5 μm section of multicellular structures formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE), and solidified with HistogelTM; [vii] cytospin and immunofluorescence of E-cadherin (green) and nuclear staining with DAPI (blue); asterisks, spheroidal multicellular structures; squares, irregular multicellular structures. (B) Non-adherent multicellular structures were fixed, solidified in HistogelTM, embedded in paraffin, and subjected to immunocytochemical staining for E-Cadherin [i], CA125 [ii], or p53 [iii]. (C) A spheroidal multicellular structure is observed using phase-contrast microscopy when floating [i], after attachment [ii], and after further development in culture [iii], giving rise to newly formed multicellular structures [iv]. Asterisk, spheroidal multicellular structures; square, multicellular foci; arrowheads, cellular structures that remain adherent to the plastic surface. Scale bars in B and C, 50 μm.