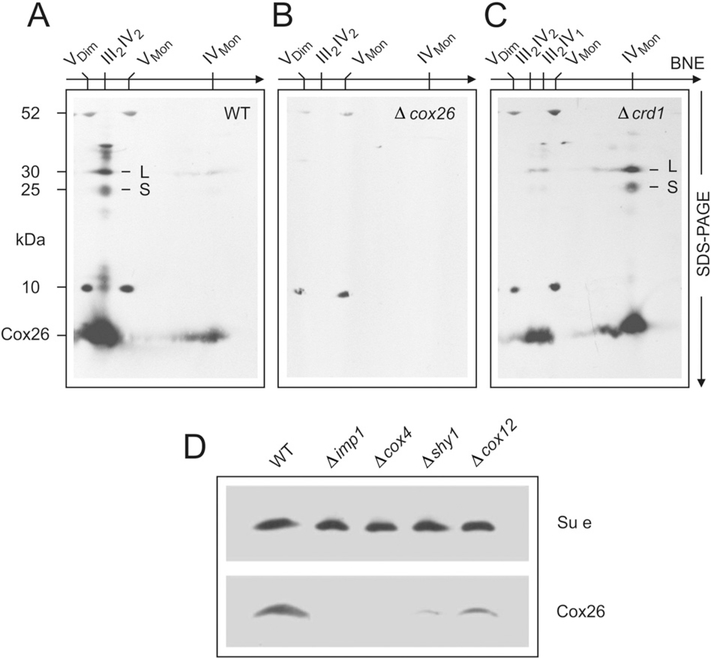
Fig. 5.
Cox26 protein is associated with complex IV. Assignment of complexes as in Fig. 1. Digitonin-solubilized mitochondrial complexes from (A) wild type yeast, (B) Δcox26 strain, and (C) Δcrd1 mutant with defective cardiolipin synthase were separated by BNE, followed by Tricine-SDS-PAGE in the second dimension using 13% acrylamide gels for Tricine-SDS-PAGE and electroblotted onto PVDF membranes. Anti-Cox26 antibody identified Cox26 (6.4 kDa) and two larger bands, L and S, with apparent masses around 25 kDa and 30 kDa, in the column of subunits of supercomplexes (e.g. in Figure partA). It also identified monomeric complex IV, e.g. in the Δcrd1 strain (figure partC). Detection of10 kDa and 52 kDa subunits of complex V seemed non-specific cross-reactions by the Cox26 antibody that mark the position of the monomeric and dimeric ATP synthase complexes. (D) Estimation of Cox26 protein amounts in null mutant strains not containing assembled complex IV (Δimp1 and Δcox4) or containing reduced amounts of complex IV (Δshy1 and Δcox12). Complex V amounts were estimated by a specific anti-subunit e antibody as loading control.