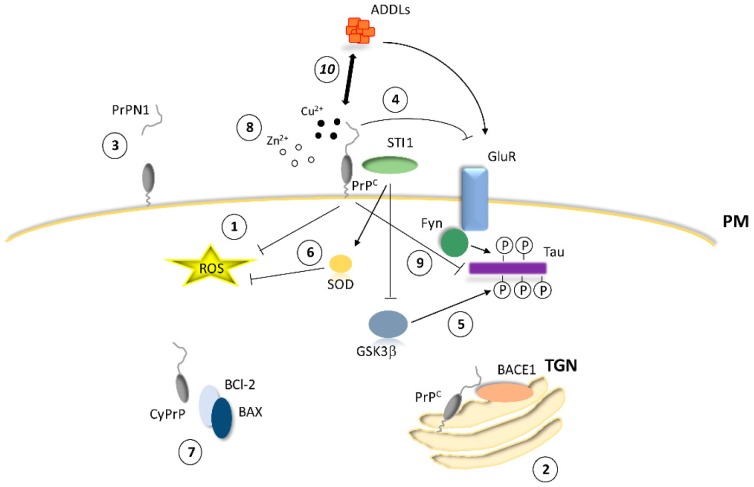
Figure 4.
Proposal of a putative scenario for neuroprotective intervention of PrPC in AD: 1. Modulating ROS levels; 2. Inhibiting BACE1 activity; 3. Generating PrPN1; 4. Modulating glutamate receptors (both ionotropic (NMDAR) and metabotropic (mGluR5)); 5. Reducing phospho-tau levels through STI-1 interaction and GSK3β inhibition; 6. Reducing ROS levels through STI-1 interaction and consequent SOD modulation; 7. Executing anti-Bax activity; 8. Increasing Zn2+ uptake; and 9. Reducing tau levels. Number 10, in italics, represents the direct intervention of ADDLs in PrPC function, inhibiting its endocytosis and/or homodimerization, and competing with Cu2+ binding and homeostasis. TGN: Trans-Golgi Network.