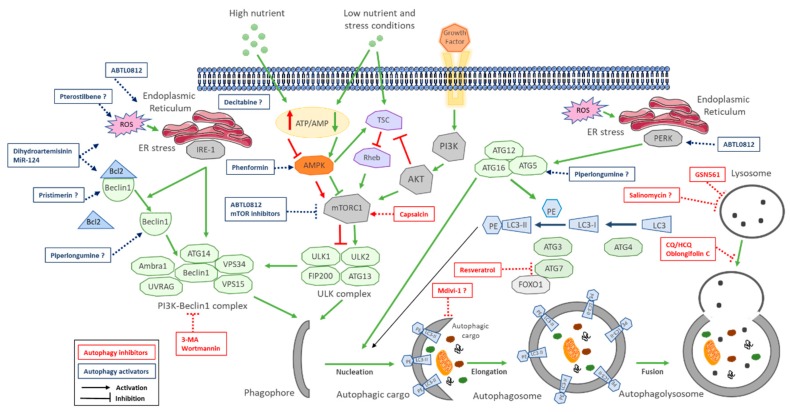
Figure 2.
Schematic overview of the autophagy molecular pathway and target steps of its modulation. Upon nutrient or energy deprivation, AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is activated, leading to mTORC1 inhibition and autophagy induction. Stress conditions activate the UPR (Unfolded Protein Response) mediated by PERK and IRE-1, which leads to the activation of autophagy. The ULK complex consists in ULK1, ULK2, FIP200 and ATG13. The PI3K-Beclin1 complex consists in VPS34, VPS15, Beclin1 and ATG14, or VPS34, Beclin1, UVRAG and Ambra1. These complexes mediate the generation of lipidated LC3 (LC3-II) and its incorporation into the phagophore membrane. The elongation of the phagophore ultimately closes and forms the autophagosome, which internalizes autophagosome cargo and fuses with lysosomes for cargo degradation and nutrient recycling. Current approaches to modulate autophagy in CCA target different steps. Autophagy inhibitors focus on inhibiting the last step, interfering with lysosome fusion or function, but other compounds target mTORC1 or other initiation steps. Autophagy activators act through targeting initial steps of autophagy, mTOR inhibition or ER-stress-induced autophagy.