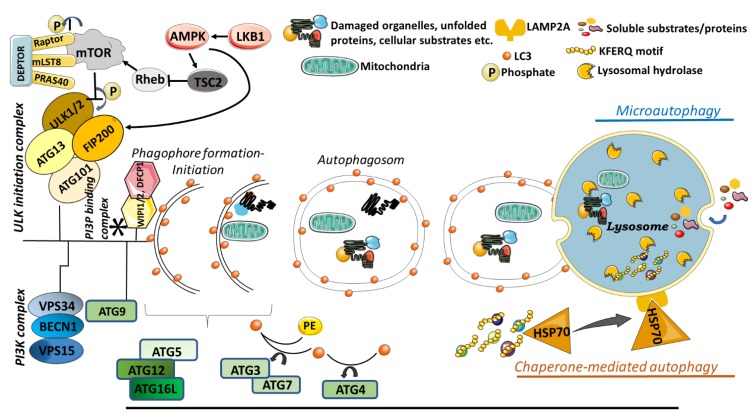
Figure 2.
Illustration of main autophagy pathways. In macroautophagy, cellular contents are engulfed by double membrane vesicles called as autophagosome and carried to lysosome for degradation. In microutophagy, cytosolic components are directly taken into lysosome by lysosomal membrane invagination and degraded. In CMA, chaperon guiding proteins recognize target proteins and carry them to lysosome for degradation. mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin protein, a highly conserved serine/threonine kinase, ULK1: Unc-51 Like Autophagy Activating Kinase 1, ULK2: Unc-51 Like Autophagy Activating Kinase 2 kinase, FIP200: focal adhesion kinase-family interacting protein of 200 kDa, PI3K: Complex of class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases, PI3P: Phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate, AMPK: AMP-activated kinase, LKB1: liver kinase B1, Rheb: Ras-related small G protein, TSC2: tuberous sclerosis complex 2, VPS34: vacuolar protein sorting 34, VPS15: vacuolar protein sorting 15, BECN1: Beclin-1, PE: phosphatidylethanolamine, LC3: microtubule-associated protein light chain 3, WIPI: WD repeat domain phosphoinositide-interacting protein, DFCP1: Double FYVE-containing protein 1. In the figure, arrows indicate activation, whereas bars show inhibition.