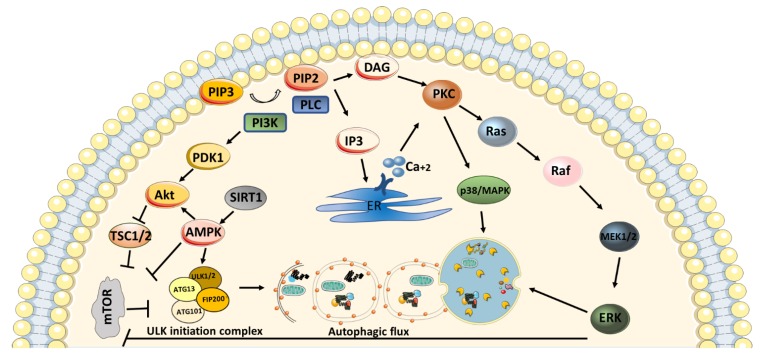
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of main signaling pathways playing role in autophagy activation. In the figure, arrows indicate activation, whereas bars show inhibition. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) results in dephosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol [3,4,5]-trisphosphate (PIP3) and generates phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate (PIP2). Phospholipase C (PLC) hydrolyses PIP2 and produces inositol-1, 4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG). IP3 translocates to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in order to release calcium. DAG and calcium binding activate protein kinase C (PKC). Activation of PKC stimulates downstream signaling pathways; mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38/MAPK) and RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathways for autophagy regulation. Also, PI3K mediates initiation of Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway for inhibition of autophagy by suppressing Unc-51 Like autophagy activating kinase (ULK) complex. Activation of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and silence information regulator 1 (SIRT1) causes activation of autophagy through both suppression of mTOR or activation of Akt or ULK initiation complex.