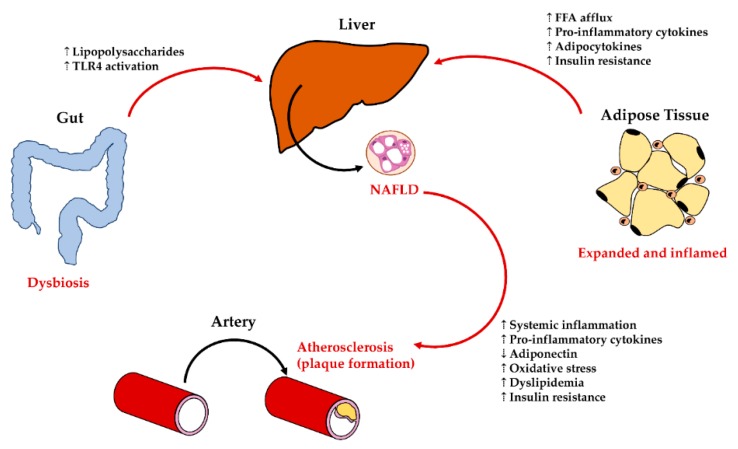
Figure 4.
Interaction of liver damage with extra-hepatic organs. NAFLD is influences by interaction with other organs/tissues. Adipose tissue disarrangement (expansion/inflammation) induces increased Free Fatty Acid (FFA) afflux to the liver and insulin resistance; moreover, it releases several pro-inflammatory cytokines and modifies the adipocytokine balance. Dysbiosis in the gut results in translocation of endotoxins (i.e., lipopolysaccharides) to the liver and the subsequent activation of the Toll-like Receptor (TLR) pathway in the liver. In turn, liver with NAFLD/NASH can influence atherosclerosis (plaque formation) by several mechanisms, including, but not limited to, systemic inflammation and oxidative stress increase.