Figure 1.
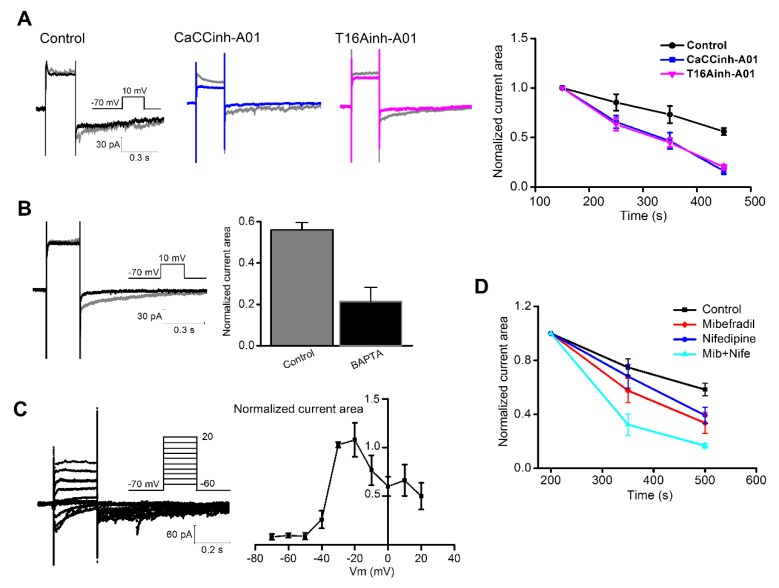
Relationship between Ca2+-dependent characteristics of the TMEM16A/anoctamin1 (ANO1) current and voltage-gated Ca2+ channel (VGCC). (A) Rod bipolar cells were stimulated from a holding potential of −70 mV to a membrane potential 10 mV for 250 ms. Representative current traces before (gray) and 300 s after drug administration (black, blue, pink). The current area was normalized by the area of Itail at 150 s, and the normalized current area over time (right) showed the inhibitory effect of ANO1-specific blockers (n = 7; p < 0.05, Student’s t-test). (B) Internal application of 5 mM BAPTA (black; 0.56 ± 0.03) decreased Itail compared with the control (gray; 0.21 ± 0.06; n = 7; p < 0.05, Student’s t-test). (C) Rod bipolar cells were stimulated from a holding potential of −70 to −60 mV until approximately 20 mV. Current traces (left) and the normalized current area of Itail (right) against command voltage were plotted. (D) The current area was normalized by the area of Itail at 200 s, and the normalized current area over time showed the inhibitory effects of L- and T-type VGCC inhibitors, namely 40 μM nifedipine and 40 μM mibefradil, respectively (n = 7; ANOVA, p < 0.05).