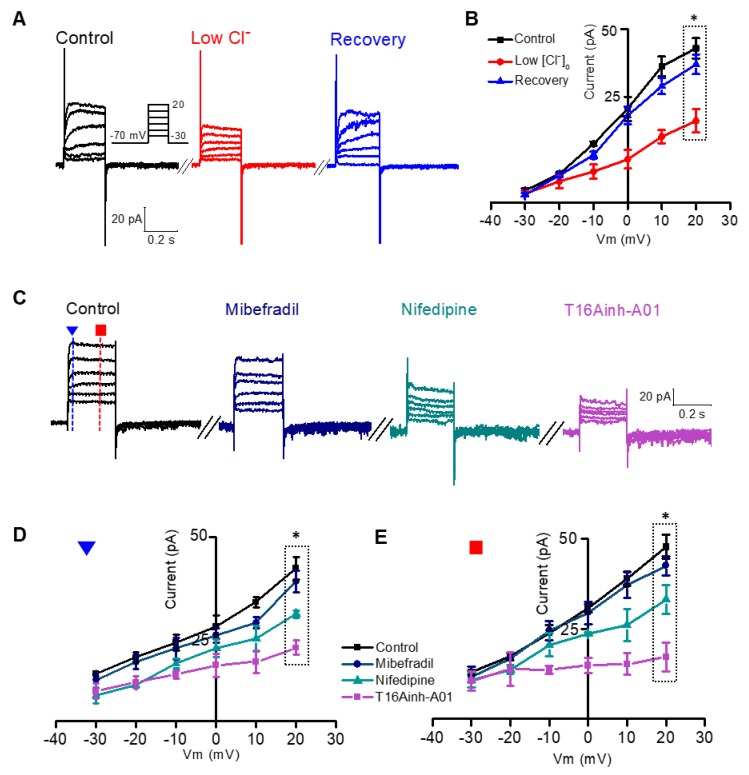
Figure 2.
Isolation of the voltage-dependent component of ANO1 in rod bipolar cells. Isolation of the outwardly rectifying ANO1 component with strong voltage dependence. (A) In a single rod bipolar cell lacking Itail, a family of whole-cell currents was serially recorded to monitor the changes in outward current as [Cl−]o changes. First, voltage-clamp (−30 to 20 mV for 250 ms) was performed under 140 mM of [Cl−]o (black). Next, a family of whole-cell current was recorded after the extracellular replacement of Cl− with 100 mM gluconate (red) and then back to the control (blue). (B) For each of the three cases, the outward current (mean amplitudes measured at 200 ms after the onset of the depolarizing pulse) was plotted against the command voltage (n = 7, *p < 0.05, ANOVA). (C) The effects of VGCC inhibitors and ANO1-specific blocker on outward rectifying currents were plotted by recording a series of whole-cell currents. The control (black), 10 μM mibefradil (navy), 30 μM nifedipine (dark cyan), and 10 μM T16Ainh-A01 (violet) were administered in this order to the cells in bath while waiting for recovery before administration. To compare the changes in the earlier portion (blue triangle) and in the later portion (red rectangle), the amplitudes measured at 20 and 200 ms after the onset of the depolarizing pulse were plotted in (D) and (E) against the command voltage, respectively. The inhibitors significantly reduced outward currents, compared to the control (n = 6, *p < 0.05, ANOVA).