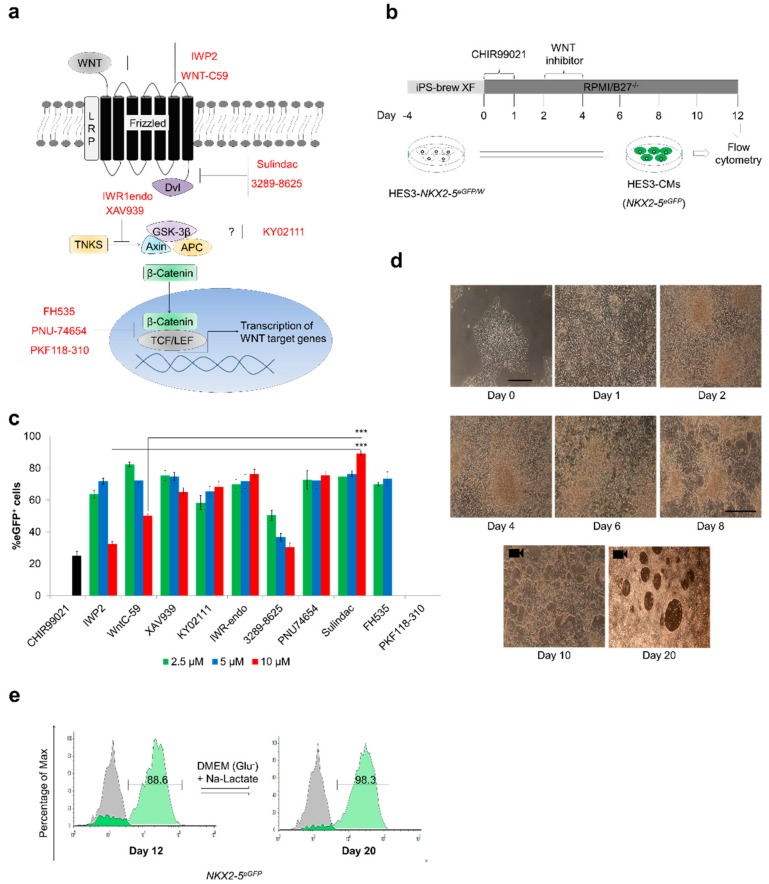
Figure 1.
Sulindac efficiently promotes cardiogenesis in human embryonic stem cells (hESCs): (a) Schematic representation of the Wnt signaling transduction pathway. When activation occurs via binding of Wnt ligand to Frizzled receptor, beta catenin translocates into the nucleus and activates transcription of Wnt target genes. Different small molecule Wnt inhibitors interact with different target proteins in Wnt pathway leading to phosphorylation and degradation of beta catenin and inhibition of transcription of Wnt target genes; (b) Protocol for in vitro cardiac differentiation using Wnt signaling modulators. Undifferentiated hPSC colonies were maintained in iPS-brew XF media from days −4 to 0. Mesendodermal differentiation was initiated in the first phase by changing the culture media to RPMI-B27-/- media containing CHIR99021 (10 μM). In the second phase, cells were cultured in the presence of Wnt inhibitors (2.5 μM, 5 μM or 10 μM) from day 2 to 4. Spontaneously beating cardiac clusters were observed from day 9 onwards; (c) Proportion of eGFP+ cells observed with different Wnt inhibitors at different concentrations from 3 independent experiments. Cardiac differentiation was carried out according to (b) and the proportion of eGFP+ cells was measured on day 12 by flow cytometry (Error bars, ±SEM; n = 3 independent biological replicates, Student’s t test, * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001); (d) Representative phase-contrast images of HES3 cells taken over the 20 day period of Sulindac-induced differentiation show pluripotent HES3 cells and cell in cardiac transition. Scale bar, 50 µm. Videos of day 10 and day 20 CMs are provided in Video-1 and Video-2 respectively; (e) Representative FACS analyses for percent eGFP+ cells before lactate treatment (day 12) and after lactate treatment (day 20). Control (Gray) indicates undifferentiated HES3 cells.