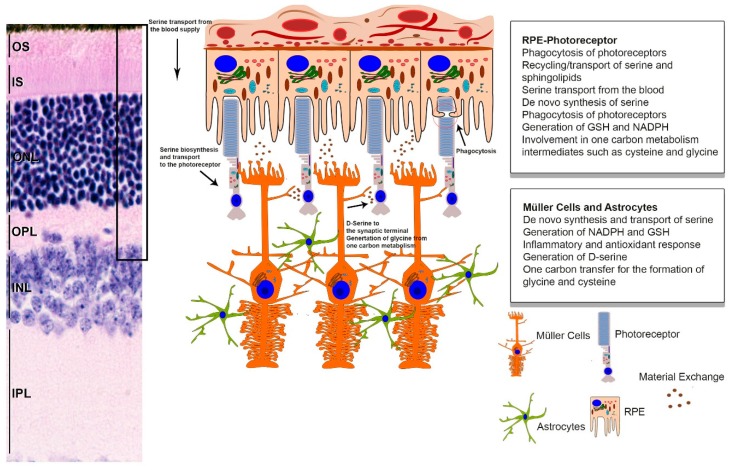
Figure 3.
Graphical summary of serine metabolism in the retina. Serine homeostasis is primarily maintained by the RPE and retinal glia. The RPE transports and generates serine, which is ultimately transported to the photoreceptors. Additionally, important serine metabolic products such as glycine and cysteine are transported or catabolized to be used as fuel, as the energetic requirements of the RPE are very high. Photoreceptors also receive serine from the Müller glia and astrocytes. Glial cells are vital to the macula and generate serine from glycolysis, which is crucial in maintaining the redox balance in the photoreceptors, controlling neurotransmission, and mediating inflammation response elements. (IS, inner segment; OS, outer segment; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer).